GF Resource Grammar Library: Synopsis
Introduction
The GF Resource Grammar Library is the standard library for Grammatical Framework. It covers the morphology and basic syntax of currently 38 languages: Afrikaans, Arabic, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese (simplified), Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Basque, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hindi, Icelandic, Italian, Japanese, Latin, Latvian, Maltese, Mongolian, Nepali, Norwegian (nynorsk), Norwegian (bokmål), Persian, Punjabi, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Slovak, Sindhi, Spanish, Swedish, Thai, Urdu.
This document contains the most important parts of the GF Resource Grammar API, as needed by a GF application programmer. It has been machine-generated from the source files; there are links to the relevant source files, which give more information. Some of the files have not yet been prepared so that the machine generated documentation has the nicest possible format.
The main contents are:
- Chapter 1: categories, with links to the functions for constructing trees in them.
- Chapter 2: syntactic construction functions, with cross-links and examples.
- Chapter 3: morphological (lexical) paradigms.
- Chapter 4: additional libraries.
- Chapter 5: how to "browse" the library by loading the grammars into the
gfcommand editor. - Chapter 6: a brief example of how application grammars can use the resource modules.
- Detailed table of contents.
The RGL Browser tool allows you to interactively browse through the library, view all functions in a module's scope, and quickly jump to their definitions.
Other relevant documents:
- The RGL Status Document: the current status of different languages and the authors of each grammar
- The Resource Grammar Library coverage map
- RGL Documentation and Publications: links to publications and other documentation
- More modules: extra modules, dictionaries, and the internals of the resource grammar
- Internal abstract syntax: synopsis of internal abstract functions and their Universal Dependency labels
- Minibar: find resource grammar expressions by parsing (select Grammar: LibraryBrowser) or test translations between all languages (select Grammar: ResourceDemo)
- Resource Grammar Tutorial, as previously presented in LREC-2010.
- Paper "The GF Resource Grammar Library" by A. Ranta (Linguistic Issues in Language Technology, 2 (2), 2009). An overview of the library with linguistic motivations. PDF
- Paper "Grammars as Software Libraries" by A. Ranta (In Y. Bertot, G. Huet, J-J. Lévy, and G. Plotkin (eds.), From Semantics to Computer Science, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 281--308, 2009). The library from a software engineering point of view. PDF
Categories
Source 1: ../../src/abstract/Common.gf
Source 2: ../../src/abstract/Cat.gf
A hierarchic view
The chart below shows the categories in a hierarchical top-down order. The edges do not define the complete dependency structure; if they did, the graph would have many many more edges, and also many cycles. The precise meaning of a directed edge from C to D is: there is a constructor of C that takes D as an argument. What the constructors exactly are, and what other arguments they take, is described by separate tables for each category.
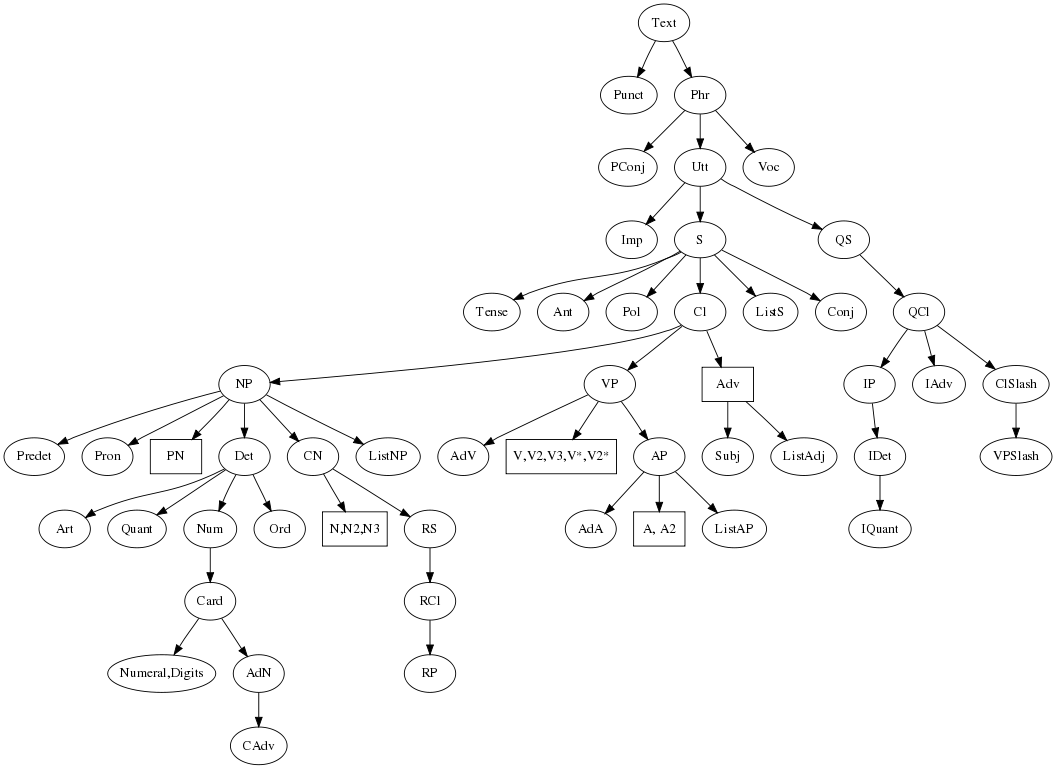
The rectangular boxes mark open lexical categories, which have constructors also in the Paradigms modules.
Explanations
| Category | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A | one-place adjective | warm |
| A2 | two-place adjective | divisible |
| ACard | adjective like cardinal | few", "many |
| AP | adjectival phrase | very warm |
| AdA | adjective-modifying adverb | very |
| AdN | numeral-modifying adverb | more than |
| AdV | adverb directly attached to verb | always |
| Adv | verb-phrase-modifying adverb | in the house |
| Ant | anteriority | simultaneous, anterior |
| CAdv | comparative adverb | more |
| CN | common noun (without determiner) | red house |
| Card | cardinal number | seven |
| Cl | declarative clause, with all tenses | she looks at this |
| Comp | complement of copula, such as AP | very warm |
| Conj | conjunction | and |
| DAP | determiner with adjective | three small |
| Det | determiner phrase | those seven |
| Digits | cardinal or ordinal in digits | 1,000/1,000th |
| IAdv | interrogative adverb | why |
| IComp | interrogative complement of copula | where |
| IDet | interrogative determiner | how many |
| IP | interrogative pronoun | who |
| Imp | imperative | look at this |
| Interj | interjection | alas |
| N | common noun | house |
| N2 | relational noun | son |
| N3 | three-place relational noun | connection |
| NP | noun phrase (subject or object) | the red house |
| Num | number determining element | seven |
| Numeral | cardinal or ordinal in words | five/fifth |
| Ord | ordinal number (used in Det) | seventh |
| PConj | phrase-beginning conjunction | therefore |
| PN | proper name | Paris |
| Phr | phrase in a text | but be quiet please |
| Pol | polarity | positive, negative |
| Predet | predeterminer (prefixed Quant) | all |
| Prep | preposition, or just case | in |
| Pron | personal pronoun | she |
| QCl | question clause, with all tenses | why does she walk |
| QS | question | where did she live |
| Quant | quantifier ('nucleus' of Det) | this/these |
| RCl | relative clause, with all tenses | in which she lives |
| RP | relative pronoun | in which |
| RS | relative | in which she lived |
| S | declarative sentence | she lived here |
| SC | embedded sentence or question | that it rains |
| Subj | subjunction | if |
| Temp | temporal and aspectual features | past anterior |
| Tense | tense | present, past, future |
| Text | text consisting of several phrases | He is here. Why? |
| Utt | sentence, question, word... | be quiet |
| V | one-place verb | sleep |
| V2 | two-place verb | love |
| V2A | verb with NP and AP complement | paint |
| V2Q | verb with NP and Q complement | ask |
| V2S | verb with NP and S complement | tell |
| V2V | verb with NP and V complement | cause |
| V3 | three-place verb | show |
| VA | adjective-complement verb | look |
| VP | verb phrase | is very warm |
| VPSlash | verb phrase missing complement | give to John |
| VQ | question-complement verb | wonder |
| VS | sentence-complement verb | claim |
| VV | verb-phrase-complement verb | want |
| Voc | vocative or "please" | my darling |
Syntax Rules and Structural Words
Source 1: ../../src/api/Constructors.gf
Source 2: ../../src/abstract/Structural.gf
A - one-place adjective
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
A2 - two-place adjective
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
ACard - adjective like cardinal
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
AP - adjectival phrase
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
comparAP |
A -> AP |
warmer
|
mkAP |
A -> AP |
warm
|
mkAP |
A -> NP -> AP |
warmer than Paris
|
mkAP |
A2 -> NP -> AP |
married to her
|
mkAP |
A2 -> AP |
married
|
mkAP |
AP -> S -> AP |
it is good that she sleeps
|
mkAP |
AP -> QS -> AP |
it is uncertain who sleeps
|
mkAP |
AP -> VP -> AP |
she is ready to sleep
|
mkAP |
AP -> SC -> AP |
she is ready to sleep
|
mkAP |
AdA -> A -> AP |
very old
|
mkAP |
AdA -> AP -> AP |
very very old
|
mkAP |
Conj -> AP -> AP -> AP |
old or young
|
mkAP |
Conj -> ListAP -> AP |
old, big and warm
|
mkAP |
Ord -> AP |
oldest
|
mkAP |
CAdv -> AP -> NP -> AP |
as old as she
|
reflAP |
A2 -> AP |
married to itself
|
AdA - adjective-modifying adverb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
almost_AdA |
AdA |
almost red
|
quite_Adv |
AdA |
quite
|
so_AdA |
AdA |
so warm
|
too_AdA |
AdA |
too warm
|
very_AdA |
AdA |
very warm
|
AdN - numeral-modifying adverb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
almost_AdN |
AdN |
almost eight
|
at_least_AdN |
AdN |
at least eight
|
at_most_AdN |
AdN |
at most eight
|
mkAdN |
CAdv -> AdN |
more than eight
|
AdV - adverb directly attached to verb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
always_AdV |
AdV |
always
|
Adv - verb-phrase-modifying adverb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
everywhere_Adv |
Adv |
everywhere
|
here7from_Adv |
Adv |
from here
|
here7to_Adv |
Adv |
to here
|
here_Adv |
Adv |
here
|
mkAdv |
A -> Adv |
warmly
|
mkAdv |
Prep -> NP -> Adv |
in the house
|
mkAdv |
Subj -> S -> Adv |
when she sleeps
|
mkAdv |
CAdv -> A -> NP -> Adv |
more warmly than he
|
mkAdv |
CAdv -> A -> S -> Adv |
more warmly than he runs
|
mkAdv |
AdA -> Adv -> Adv |
very warmly
|
mkAdv |
Conj -> Adv -> Adv -> Adv |
here and now
|
mkAdv |
Conj -> ListAdv -> Adv |
with her, here and now
|
somewhere_Adv |
Adv |
somewhere
|
there7from_Adv |
Adv |
from there
|
there7to_Adv |
Adv |
there
|
there_Adv |
Adv |
there
|
Ant - anteriority
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
anteriorAnt |
Ant |
she has slept
|
simultaneousAnt |
Ant |
she sleeps
|
CAdv - comparative adverb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
as_CAdv |
CAdv |
as
|
less_CAdv |
CAdv |
less
|
more_CAdv |
CAdv |
more
|
CN - common noun (without determiner)
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkCN |
N -> CN |
house
|
mkCN |
N2 -> NP -> CN |
mother of the king
|
mkCN |
N3 -> NP -> NP -> CN |
distance from this city to Paris
|
mkCN |
N2 -> CN |
mother
|
mkCN |
N3 -> CN |
distance
|
mkCN |
A -> N -> CN |
big house
|
mkCN |
A -> CN -> CN |
big blue house
|
mkCN |
AP -> N -> CN |
very big house
|
mkCN |
AP -> CN -> CN |
very big blue house
|
mkCN |
N -> RS -> CN |
man that she loves
|
mkCN |
CN -> RS -> CN |
old man that she loves
|
mkCN |
N -> Adv -> CN |
house on the hill
|
mkCN |
CN -> Adv -> CN |
big house on the hill
|
mkCN |
CN -> S -> CN |
rule that she sleeps
|
mkCN |
CN -> QS -> CN |
question if she sleeps
|
mkCN |
CN -> VP -> CN |
reason to sleep
|
mkCN |
CN -> SC -> CN |
reason to sleep
|
mkCN |
N -> NP -> CN |
king John
|
mkCN |
CN -> NP -> CN |
old king John
|
Card - cardinal number
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkCard |
Str -> Card |
thirty-five (given as "35"; range 1-999) |
mkCard |
Numeral -> Card |
seven
|
mkCard |
Digits -> Card |
51 |
mkCard |
AdN -> Card -> Card |
almost fifty |
Cl - declarative clause, with all tenses
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
genericCl |
VP -> Cl |
one sleeps
|
mkCl |
NP -> V -> Cl |
she sleeps
|
mkCl |
NP -> V2 -> NP -> Cl |
she loves him
|
mkCl |
NP -> V3 -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
she sends it to him
|
mkCl |
NP -> VV -> VP -> Cl |
she wants to sleep
|
mkCl |
NP -> VS -> S -> Cl |
she says that I sleep
|
mkCl |
NP -> VQ -> QS -> Cl |
she wonders who sleeps
|
mkCl |
NP -> VA -> A -> Cl |
she becomes old
|
mkCl |
NP -> VA -> AP -> Cl |
she becomes very old
|
mkCl |
NP -> V2A -> NP -> A -> Cl |
she paints it red
|
mkCl |
NP -> V2A -> NP -> AP -> Cl |
she paints it red
|
mkCl |
NP -> V2S -> NP -> S -> Cl |
she answers to him that we sleep
|
mkCl |
NP -> V2Q -> NP -> QS -> Cl |
she asks him who sleeps
|
mkCl |
NP -> V2V -> NP -> VP -> Cl |
she begs him to sleep
|
mkCl |
NP -> VPSlash -> NP -> Cl |
she begs him to sleep here |
mkCl |
NP -> A -> Cl |
she is old
|
mkCl |
NP -> A -> NP -> Cl |
she is older than he
|
mkCl |
NP -> A2 -> NP -> Cl |
she is married to him
|
mkCl |
NP -> AP -> Cl |
she is very old
|
mkCl |
NP -> NP -> Cl |
she is the woman
|
mkCl |
NP -> N -> Cl |
she is a woman
|
mkCl |
NP -> CN -> Cl |
she is an old woman
|
mkCl |
NP -> Adv -> Cl |
she is here
|
mkCl |
NP -> VP -> Cl |
she always sleeps
|
mkCl |
N -> Cl |
there is a house
|
mkCl |
CN -> Cl |
there is an old house
|
mkCl |
NP -> Cl |
there are many houses
|
mkCl |
NP -> RS -> Cl |
it is she that sleeps
|
mkCl |
Adv -> S -> Cl |
it is here that she sleeps
|
mkCl |
V -> Cl |
it rains
|
mkCl |
VP -> Cl |
it is raining
|
mkCl |
SC -> VP -> Cl |
that she sleeps is good
|
ClSlash
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkClSlash |
NP -> VPSlash -> ClSlash |
whom does she see
|
mkClSlash |
NP -> V2 -> ClSlash |
whom does she see
|
mkClSlash |
NP -> VV -> V2 -> ClSlash |
whom does she want to see
|
mkClSlash |
Cl -> Prep -> ClSlash |
whom does she sleep with
|
mkClSlash |
ClSlash -> Adv -> ClSlash |
whom does she see today
|
mkClSlash |
NP -> VS -> SSlash -> ClSlash |
whom does she know that we hadn't seen
|
Comp - complement of copula, such as AP
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkComp |
AP -> Comp |
to be old
|
mkComp |
NP -> Comp |
to be this man
|
mkComp |
Adv -> Comp |
to be here
|
Conj - conjunction
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
and_Conj |
Conj |
here and now
|
both7and_DConj |
Conj |
both here and there
|
either7or_DConj |
Conj |
either here or there
|
if_then_Conj |
Conj |
if here then there
|
or_Conj |
Conj |
here or there
|
DAP - determiner with adjective
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
Det - determiner phrase
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
aPl_Det |
Det |
women
|
aSg_Det |
Det |
a woman
|
a_Det |
Det |
a house
|
every_Det |
Det |
every woman
|
few_Det |
Det |
few women
|
many_Det |
Det |
many houses
|
mkDet |
Quant -> Det |
this
|
mkDet |
Quant -> Card -> Det |
these five
|
mkDet |
Quant -> Ord -> Det |
the fifth
|
mkDet |
Quant -> Num -> Ord -> Det |
the five best
|
mkDet |
Quant -> Num -> Det |
these
|
mkDet |
Card -> Det |
five
|
mkDet |
Digits -> Det |
51 |
mkDet |
Numeral -> Det |
five |
mkDet |
Pron -> Det |
my |
mkDet |
Pron -> Num -> Det |
my five
|
much_Det |
Det |
much wine
|
somePl_Det |
Det |
some women
|
someSg_Det |
Det |
some wine
|
that_Det |
Det |
that woman
|
thePl_Det |
Det |
the houses
|
theSg_Det |
Det |
the house
|
the_Det |
Det |
the house
|
these_Det |
Det |
these women
|
this_Det |
Det |
this woman
|
those_Det |
Det |
those women
|
Dig
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
n0_Dig |
Dig | 0 |
n1_Dig |
Dig | 1 |
n2_Dig |
Dig | 2 |
n3_Dig |
Dig | 3 |
n4_Dig |
Dig | 4 |
n5_Dig |
Dig | 5 |
n6_Dig |
Dig | 6 |
n7_Dig |
Dig | 7 |
n8_Dig |
Dig | 8 |
n9_Dig |
Dig | 9 |
Digits - cardinal or ordinal in digits
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkDigits |
Str -> Digits |
35 (from string "35"; ; range 1-9999999) |
mkDigits |
Dig -> Digits |
4
|
mkDigits |
Dig -> Digits -> Digits |
1,233,486
|
IAdv - interrogative adverb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
how8much_IAdv |
IAdv |
how much
|
how_IAdv |
IAdv |
how
|
mkIAdv |
Prep -> IP -> IAdv |
in which city
|
mkIAdv |
IAdv -> Adv -> IAdv |
where in Paris
|
when_IAdv |
IAdv |
when
|
where_IAdv |
IAdv |
where
|
why_IAdv |
IAdv |
why
|
IComp - interrogative complement of copula
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkIComp |
IAdv -> IComp |
where (is it) |
mkIComp |
IP -> IComp |
who (is it) |
IDet - interrogative determiner
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
how8many_IDet |
IDet |
how many houses
|
mkIDet |
IQuant -> Num -> IDet |
which houses
|
mkIDet |
IQuant -> IDet |
which house
|
whichPl_IDet |
IDet |
which houses
|
which_IDet |
IDet |
which house
|
IP - interrogative pronoun
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkIP |
IDet -> CN -> IP |
which five big cities
|
mkIP |
IDet -> N -> IP |
which five cities
|
mkIP |
IDet -> IP |
which five
|
mkIP |
IQuant -> CN -> IP |
which big city
|
mkIP |
IQuant -> Num -> CN -> IP |
which five big cities
|
mkIP |
IQuant -> N -> IP |
which city
|
mkIP |
IP -> Adv -> IP |
who in Paris
|
whatPl_IP |
IP |
what
|
whatSg_IP |
IP |
what
|
what_IP |
IP |
what
|
whoPl_IP |
IP |
who
|
whoSg_IP |
IP |
who
|
who_IP |
IP |
who
|
IQuant
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
which_IQuant |
IQuant |
which house
|
Imp - imperative
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkImp |
VP -> Imp |
come to my house
|
mkImp |
V -> Imp |
come
|
mkImp |
V2 -> NP -> Imp |
buy it
|
ImpForm
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
pluralImpForm |
ImpForm |
be men
|
politeImpForm |
ImpForm |
be a man
|
singularImpForm |
ImpForm |
be a man
|
Interj - interjection
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
ListAP
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkListAP |
AP -> AP -> ListAP |
list of two |
mkListAP |
AP -> ListAP -> ListAP |
list of more |
ListAdv
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkListAdv |
Adv -> Adv -> ListAdv |
list of two |
mkListAdv |
Adv -> ListAdv -> ListAdv |
list of more |
ListNP
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkListNP |
NP -> NP -> ListNP |
list of two |
mkListNP |
NP -> ListNP -> ListNP |
list of more |
ListRS
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkListRS |
RS -> RS -> ListRS |
list of two |
mkListRS |
RS -> ListRS -> ListRS |
list of more |
ListS
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkListS |
S -> S -> ListS |
list of two |
mkListS |
S -> ListS -> ListS |
list of more |
N - common noun
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
N2 - relational noun
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
N3 - three-place relational noun
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
NP - noun phrase (subject or object)
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
everybody_NP |
NP |
everybody
|
everything_NP |
NP |
everything
|
he_NP |
NP |
he
|
i_NP |
NP |
I
|
it_NP |
NP |
it
|
mkNP |
Quant -> N -> NP |
this man
|
mkNP |
Quant -> CN -> NP |
this old man
|
mkNP |
Quant -> Num -> CN -> NP |
these five old men
|
mkNP |
Quant -> Num -> N -> NP |
these five men
|
mkNP |
Det -> CN -> NP |
the five old men
|
mkNP |
Det -> N -> NP |
the five men
|
mkNP |
Numeral -> CN -> NP |
five old men
|
mkNP |
Numeral -> N -> NP |
five men
|
mkNP |
Digits -> CN -> NP |
51 old men
|
mkNP |
Digits -> N -> NP |
51 men
|
mkNP |
Card -> CN -> NP |
forty-five old men |
mkNP |
Card -> N -> NP |
forty-five men |
mkNP |
Pron -> CN -> NP |
my old man
|
mkNP |
Pron -> N -> NP |
my man
|
mkNP |
PN -> NP |
Paris
|
mkNP |
Pron -> NP |
we
|
mkNP |
Quant -> NP |
this
|
mkNP |
Quant -> Num -> NP |
these five
|
mkNP |
Det -> NP |
the five best
|
mkNP |
CN -> NP |
old beer
|
mkNP |
N -> NP |
beer
|
mkNP |
Predet -> NP -> NP |
only this woman
|
mkNP |
NP -> V2 -> NP |
the man seen
|
mkNP |
NP -> Adv -> NP |
Paris today
|
mkNP |
NP -> RS -> NP |
John, that walks ...
|
mkNP |
Conj -> NP -> NP -> NP |
this woman or John
|
mkNP |
Conj -> ListNP -> NP |
this woman, John or I
|
nobody_NP |
NP |
nobody
|
nothing_NP |
NP |
nothing
|
she_NP |
NP |
she
|
somebody_NP |
NP |
somebody
|
something_NP |
NP |
something
|
that_NP |
NP |
that
|
these_NP |
NP |
these
|
they_NP |
NP |
they
|
this_NP |
NP |
this
|
those_NP |
NP |
those
|
we_NP |
NP |
we
|
youPl_NP |
NP |
you
|
youPol_NP |
NP |
you
|
you_NP |
NP |
you
|
Num - number determining element
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkNum |
Str -> Num |
thirty-five (given by "35"; range 1-999) |
mkNum |
Numeral -> Num |
...
|
mkNum |
Digits -> Num |
21
|
mkNum |
Digit -> Num |
five |
mkNum |
Card -> Num |
almost five
|
mkNum |
AdN -> Card -> Num |
almost five
|
pluralNum |
Num | plural |
singularNum |
Num | singular |
Numeral - cardinal or ordinal in words
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkNumeral |
Unit -> Numeral |
eight (coerce 1..9) |
mkNumeral |
Sub100 -> Numeral |
twenty-five (coerce 1..99) |
mkNumeral |
Sub1000 -> Numeral |
nine hundred and ...
|
mkNumeral |
Sub1000 -> Sub1000 -> Numeral |
nine hundred and ...
|
mkNumeral |
Str -> Numeral |
thirty-five (given by "35"; range 1-999) |
thousandfoldNumeral |
Sub1000 -> Numeral |
nine hundred and ...
|
Ord - ordinal number (used in Det)
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkOrd |
Numeral -> Ord |
twentieth |
mkOrd |
Digits -> Ord |
51st |
mkOrd |
Digit -> Ord |
fifth |
mkOrd |
A -> Ord |
smallest
|
PConj - phrase-beginning conjunction
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
but_PConj |
PConj |
but
|
mkPConj |
Conj -> PConj |
and now
|
otherwise_PConj |
PConj |
otherwise
|
therefore_PConj |
PConj |
therefore
|
PN - proper name
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
Phr - phrase in a text
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkPhr |
(PConj) -> Utt -> (Voc) -> Phr |
but sleep, my friend
|
mkPhr |
S -> Phr |
she won't sleep
|
mkPhr |
Cl -> Phr |
she sleeps
|
mkPhr |
QS -> Phr |
would she sleep
|
mkPhr |
Imp -> Phr |
sleep
|
Pol - polarity
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
negativePol |
Pol |
she doesn't sleep
|
positivePol |
Pol |
she sleeps
|
Predet - predeterminer (prefixed Quant)
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
all_Predet |
Predet |
all the men
|
most_Predet |
Predet |
most
|
not_Predet |
Predet |
not everybody
|
only_Predet |
Predet |
only
|
Prep - preposition, or just case
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
above_Prep |
Prep |
above it
|
after_Prep |
Prep |
after it
|
before_Prep |
Prep |
before it
|
behind_Prep |
Prep |
behind it
|
between_Prep |
Prep |
between you and me
|
by8agent_Prep |
Prep |
by it
|
by8means_Prep |
Prep |
by it
|
during_Prep |
Prep |
during it
|
except_Prep |
Prep |
except it
|
for_Prep |
Prep |
for it
|
from_Prep |
Prep |
from it
|
in8front_Prep |
Prep |
in front of it
|
in_Prep |
Prep |
in it
|
on_Prep |
Prep |
on it
|
part_Prep |
Prep |
of it
|
possess_Prep |
Prep |
of it
|
through_Prep |
Prep |
through it
|
to_Prep |
Prep |
to it
|
under_Prep |
Prep |
under it
|
with_Prep |
Prep |
with it
|
without_Prep |
Prep |
without it
|
Pron - personal pronoun
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
he_Pron |
Pron |
he
|
i_Pron |
Pron |
I
|
it_Pron |
Pron |
it
|
she_Pron |
Pron |
she
|
they_Pron |
Pron |
they
|
we_Pron |
Pron |
we
|
youPl_Pron |
Pron |
you
|
youPol_Pron |
Pron |
you
|
youSg_Pron |
Pron |
you
|
Punct
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
exclMarkPunct |
Punct |
yes!
|
fullStopPunct |
Punct |
yes.
|
questMarkPunct |
Punct |
yes?
|
QCl - question clause, with all tenses
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkQCl |
Cl -> QCl |
does she sleep
|
mkQCl |
IP -> VP -> QCl |
who always sleeps
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V -> QCl |
who sleeps
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V2 -> NP -> QCl |
who loves her
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V3 -> NP -> NP -> QCl |
who sends it to her
|
mkQCl |
IP -> VV -> VP -> QCl |
who wants to sleep
|
mkQCl |
IP -> VS -> S -> QCl |
who says that I sleep
|
mkQCl |
IP -> VQ -> QS -> QCl |
who wonders who sleeps
|
mkQCl |
IP -> VA -> A -> QCl |
who becomes old
|
mkQCl |
IP -> VA -> AP -> QCl |
who becomes very old
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V2A -> NP -> A -> QCl |
who paints it red
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V2A -> NP -> AP -> QCl |
who paints it very red
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V2S -> NP -> S -> QCl |
who answers to him that we sleep
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V2Q -> NP -> QS -> QCl |
who asks him who sleeps
|
mkQCl |
IP -> V2V -> NP -> VP -> QCl |
who begs him to sleep
|
mkQCl |
IP -> A -> QCl |
who is old
|
mkQCl |
IP -> A -> NP -> QCl |
who is older than he
|
mkQCl |
IP -> A2 -> NP -> QCl |
who is married to him
|
mkQCl |
IP -> AP -> QCl |
who is very old
|
mkQCl |
IP -> NP -> QCl |
who is the woman
|
mkQCl |
IP -> N -> QCl |
who is a woman
|
mkQCl |
IP -> CN -> QCl |
who is an old woman
|
mkQCl |
IP -> Adv -> QCl |
who is here
|
mkQCl |
IP -> NP -> V2 -> QCl |
who is her
|
mkQCl |
IP -> ClSlash -> QCl |
whom does she love today
|
mkQCl |
IAdv -> Cl -> QCl |
why does she sleep
|
mkQCl |
Prep -> IP -> Cl -> QCl |
with whom does she sleep
|
mkQCl |
IAdv -> NP -> QCl |
where is she
|
mkQCl |
IComp -> NP -> QCl |
who is this man
|
mkQCl |
IP -> QCl |
which city is there
|
QS - question
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkQS |
(Tense) -> (Ant) -> (Pol) -> QCl -> QS |
who wouldn't have slept
|
mkQS |
Cl -> QS |
does she sleep
|
Quant - quantifier ('nucleus' of Det)
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
a_Quant |
Quant |
a house
|
mkQuant |
Pron -> Quant |
my house
|
no_Quant |
Quant |
no house
|
that_Quant |
Quant |
that house
|
the_Quant |
Quant |
the house
|
this_Quant |
Quant |
this house
|
RCl - relative clause, with all tenses
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkRCl |
RP -> VP -> RCl |
woman that always sleeps
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V -> RCl |
woman that sleeps
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V2 -> NP -> RCl |
woman that loves him
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V3 -> NP -> NP -> RCl |
woman that sends it to him
|
mkRCl |
RP -> VV -> VP -> RCl |
woman that wants to sleep
|
mkRCl |
RP -> VS -> S -> RCl |
woman that says that I sleep
|
mkRCl |
RP -> VQ -> QS -> RCl |
woman that wonders who sleeps
|
mkRCl |
RP -> VA -> A -> RCl |
woman that becomes old
|
mkRCl |
RP -> VA -> AP -> RCl |
woman that becomes very old
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V2A -> NP -> A -> RCl |
woman that paints it red
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V2A -> NP -> AP -> RCl |
woman that paints it very red
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V2S -> NP -> S -> RCl |
woman that answers to him that we sleep
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V2Q -> NP -> QS -> RCl |
woman that asks him who sleeps
|
mkRCl |
RP -> V2V -> NP -> VP -> RCl |
woman that begs him to sleep
|
mkRCl |
RP -> A -> RCl |
woman that is old
|
mkRCl |
RP -> A -> NP -> RCl |
woman that is older than he
|
mkRCl |
RP -> A2 -> NP -> RCl |
woman that is married to him
|
mkRCl |
RP -> AP -> RCl |
woman that is very old
|
mkRCl |
RP -> NP -> RCl |
woman that is the woman
|
mkRCl |
RP -> N -> RCl |
student that is a woman
|
mkRCl |
RP -> CN -> RCl |
student that is an old woman
|
mkRCl |
RP -> Adv -> RCl |
woman that is here
|
mkRCl |
RP -> NP -> V2 -> RCl |
woman that we love
|
mkRCl |
RP -> ClSlash -> RCl |
woman that she loves today
|
mkRCl |
Cl -> RCl |
such that she loves him |
RP - relative pronoun
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkRP |
Prep -> NP -> RP -> RP |
all the cities in which
|
which_RP |
RP |
which
|
RS - relative
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkRS |
(Tense) -> (Ant) -> (Pol) -> RCl -> RS |
woman that wouldn't have slept
|
mkRS |
Temp -> (Pol) -> RCl -> RS |
that wouldn't have slept |
mkRS |
Conj -> RS -> RS -> RS |
woman that sleeps or that we love
|
mkRS |
Conj -> ListRS -> RS |
who sleeps, whom I see and who sleeps |
S - declarative sentence
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkS |
(Tense) -> (Ant) -> (Pol) -> Cl -> S |
she wouldn't have slept
|
mkS |
Temp -> Pol -> Cl -> S |
she wouldn't have slept |
mkS |
Conj -> S -> S -> S |
she sleeps and I run
|
mkS |
Conj -> ListS -> S |
she sleeps, I run and you walk
|
mkS |
Adv -> S -> S |
today she sleeps
|
SC - embedded sentence or question
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkSC |
S -> SC |
that she sleeps
|
mkSC |
QS -> SC |
who sleeps
|
mkSC |
VP -> SC |
to sleep
|
SSlash
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkSSlash |
Temp -> Pol -> ClSlash -> SSlash |
she hadn't seen
|
Sub100
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkSub100 |
Unit -> Sub100 |
eight
|
mkSub100 |
Unit -> Unit -> Sub100 |
...
|
tenfoldSub100 |
Unit -> Sub100 |
eight
|
Sub1000
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkSub1000 |
Sub100 -> Sub1000 |
...
|
mkSub1000 |
Unit -> Sub1000 |
nine hundred
|
mkSub1000 |
Unit -> Sub100 -> Sub1000 |
nine hundred and ...
|
Subj - subjunction
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
although_Subj |
Subj |
although she sleeps
|
because_Subj |
Subj |
because she sleeps
|
if_Subj |
Subj |
if she sleeps
|
that_Subj |
Subj |
that she sleeps
|
when_Subj |
Subj |
when she sleeps
|
Temp - temporal and aspectual features
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkTemp |
Tense -> Ant -> Temp |
e.g. past + anterior |
Tense - tense
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
conditionalTense |
Tense |
she would sleep
|
futureTense |
Tense |
she will sleep
|
pastTense |
Tense |
she slept
|
presentTense |
Tense |
she sleeps
|
Text - text consisting of several phrases
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
emptyText |
Text | (empty text) |
mkText |
Phr -> (Punct) -> (Text) -> Text |
does she sleep? yes.
|
mkText |
Utt -> (Punct) -> (Text) -> Text |
Does she sleep? Yes. |
mkText |
S -> Text |
she slept.
|
mkText |
Cl -> Text |
she sleeps.
|
mkText |
QS -> Text |
did she sleep?
|
mkText |
(Pol) -> Imp -> Text |
don't sleep!
|
mkText |
Text -> Text -> Text |
where? here. when? now!
|
Unit
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
n1_Unit |
Unit |
one
|
n2_Unit |
Unit |
two
|
n3_Unit |
Unit |
three
|
n4_Unit |
Unit |
four
|
n5_Unit |
Unit |
five
|
n6_Unit |
Unit |
six
|
n7_Unit |
Unit |
seven
|
n8_Unit |
Unit |
eight
|
n9_Unit |
Unit |
nine
|
Utt - sentence, question, word...
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
lets_Utt |
VP -> Utt |
let's sleep
|
mkUtt |
S -> Utt |
she slept
|
mkUtt |
Cl -> Utt |
she sleeps
|
mkUtt |
QS -> Utt |
who didn't sleep
|
mkUtt |
QCl -> Utt |
who sleeps
|
mkUtt |
(ImpForm) -> (Pol) -> Imp -> Utt |
don't be men
|
mkUtt |
IP -> Utt |
who
|
mkUtt |
IAdv -> Utt |
why
|
mkUtt |
NP -> Utt |
this man
|
mkUtt |
Adv -> Utt |
here
|
mkUtt |
VP -> Utt |
to sleep
|
mkUtt |
CN -> Utt |
beer
|
mkUtt |
AP -> Utt |
good
|
mkUtt |
Card -> Utt |
five
|
no_Utt |
Utt |
no
|
yes_Utt |
Utt |
yes
|
V - one-place verb
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
V2 - two-place verb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
have_V2 |
V2 |
to have it
|
V2A - verb with NP and AP complement
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
V2Q - verb with NP and Q complement
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
V2S - verb with NP and S complement
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
V2V - verb with NP and V complement
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
V3 - three-place verb
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
VA - adjective-complement verb
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
VP - verb phrase
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkVP |
V -> VP |
to sleep
|
mkVP |
V2 -> NP -> VP |
to love him
|
mkVP |
V3 -> NP -> NP -> VP |
to send it to him
|
mkVP |
VV -> VP -> VP |
to want to sleep
|
mkVP |
VS -> S -> VP |
to know that she sleeps
|
mkVP |
VQ -> QS -> VP |
to wonder who sleeps
|
mkVP |
VA -> AP -> VP |
to become red
|
mkVP |
V2A -> NP -> AP -> VP |
to paint it red
|
mkVP |
V2S -> NP -> S -> VP |
to answer to him that she sleeps
|
mkVP |
V2Q -> NP -> QS -> VP |
to ask him who sleeps
|
mkVP |
V2V -> NP -> VP -> VP |
to beg him to sleep
|
mkVP |
A -> VP |
to be old
|
mkVP |
A -> NP -> VP |
to be older than he
|
mkVP |
A2 -> NP -> VP |
to be married to him
|
mkVP |
AP -> VP |
to be very old
|
mkVP |
N -> VP |
to be a woman
|
mkVP |
CN -> VP |
to be an old woman
|
mkVP |
NP -> VP |
to be the woman
|
mkVP |
Adv -> VP |
to be here
|
mkVP |
VP -> Adv -> VP |
to sleep here
|
mkVP |
AdV -> VP -> VP |
to always sleep
|
mkVP |
VPSlash -> NP -> VP |
to paint it black
|
mkVP |
VPSlash -> VP |
to paint itself black
|
mkVP |
Comp -> VP |
to be warm
|
passiveVP |
V2 -> VP |
to be loved
|
passiveVP |
V2 -> NP -> VP |
to be loved by her
|
progressiveVP |
VP -> VP |
to be sleeping
|
reflexiveVP |
V2 -> VP |
to love itself
|
reflexiveVP |
VPSlash -> VP |
paint itself black |
VPSlash - verb phrase missing complement
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkVPSlash |
V2 -> VPSlash |
whom does she see
|
mkVPSlash |
V3 -> NP -> VPSlash |
whom does she send it to
|
mkVPSlash |
V2A -> AP -> VPSlash |
whom does she paint red
|
mkVPSlash |
V2Q -> QS -> VPSlash |
whom does she ask where I sleep
|
mkVPSlash |
V2S -> S -> VPSlash |
whom does she answer that I sleep to
|
mkVPSlash |
V2V -> VP -> VPSlash |
whom does she beg to sleep
|
mkVPSlash |
VV -> VPSlash -> VPSlash |
whom does she want to see
|
mkVPSlash |
V2V -> NP -> VPSlash -> VPSlash |
whom does she beg me to see
|
VQ - question-complement verb
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
VS - sentence-complement verb
Lexical category, constructors given in lexical paradigms.
VV - verb-phrase-complement verb
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
can8know_VV |
VV |
to be able to sleep
|
can_VV |
VV |
to be able to sleep
|
must_VV |
VV |
have to
|
want_VV |
VV |
to want to sleep
|
Voc - vocative or "please"
| Function | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
mkVoc |
NP -> Voc |
yes, my friend
|
please_Voc |
Voc |
please
|
Lexical Paradigms
Paradigms for Afrikaans
source ../../src/afrikaans/ParadigmsAfr.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
de |
Gender | non-neutrum |
het |
Gender | neutrum |
--die |
Gender | - |
mkN |
(muis : Str) -> N |
de muis-muisen, with some predictable exceptions |
mkN |
(bit : Str) -> Gender -> N |
if gender is not predictable |
mkN |
(gat,gaten : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst-case for nouns |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition van |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
other preposition than van |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. afstand + van + naar |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
proper name |
mkA |
(vers : Str) -> A |
regular adjective |
mkA |
(sag, sagte : Str) -> A --"semi-irregular" |
- |
mkA |
(goed,goede,goeds,beter,best : Str) -> A |
irregular adjective |
invarA |
Str -> A |
adjective with just one form |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. getrouwd + met |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
van_Prep |
Prep | - |
te_Prep |
Prep | - |
mkV |
(aaien : Str) -> V |
regular verb |
mkV |
(breken,brak,gebroken : Str) -> V |
theme of irregular verb |
mkV |
(breken,brak,braken,gebroken : Str) -> V |
also past plural irregular |
mkV |
(aai,aait,aaien,aaide,aaide,aaiden,geaaid : Str) -> V |
worst-case verb |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
add movable suffix, e.g. af + stappen |
zijnV |
V -> V |
force zijn as auxiliary (default hebben) |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive verb e.g. zich afvragen |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
geven,(accusative),(dative) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
sturen,(accusative),naar |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
praten, met, over |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for Arabic
source ../../src/arabic/ParadigmsAra.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Case |
Type | Argument to mkPrep |
nom |
Case | Nominative |
acc |
Case | Accusative |
gen |
Case | Genitive |
Gender |
Type | Argument to mkN and mkPN |
masc |
Gender | Masculine |
fem |
Gender | Feminine |
Number |
Type | Argument to mkConj ("NP and NP" plural; "NP or NP" singular), and special cases of mkN, where nominal attribute is included in the N. |
sg |
Number | Singular |
pl |
Number | Plural |
Species |
Type | Argument to mkN. |
hum |
Species | Human nouns (teacher, woman, brother, …) |
nohum |
Species | Any other nouns (house, dog, …) |
Vowel |
Type | Argument to mkV, when constructing verbs of Form I. |
va |
Vowel | a (fatha) as the perfect or imperfect vowel, e.g. فعَل |
vi |
Vowel | i (kasra) as the perfect or imperfect vowel, e.g فعِل |
vu |
Vowel | u (damma) as the perfect or imperfect vowel, e.g. فعُل |
mkN |
(sg : Str) -> N |
Takes the singular without case marking, gives a non-human regular noun. Plural is sound feminine if the word ends in ة, otherwise sound masculine. |
mkN |
(sg,pl : Str) -> Gender -> Species -> N |
Takes the singular and the plural (sound or broken) forms without case marking, returns a noun with basic triptote declension. NB for irregular/weak roots, safer to use brkN, sdfN or sdmN, which take root and pattern. |
mkN |
(root,sgPat,plPat : Str) -> Gender -> Species -> N |
(This is brkN; see its description.) |
mkN |
Species -> N -> N |
Change species (hum/nohum) of a noun. |
mkN |
N -> (attr : Str) -> N |
Compound noun with invariant attribute. |
mkN |
N -> N -> N |
Compound noun with singular genitive attribute, but inflects in state. |
mkN |
Number -> N -> N -> N |
Compound noun with genitive attribute, but inflects in state. Attribute's number specified by 1st arg. |
brkN |
(root,sgPat,brokenPlPat : Str) -> Gender -> Species -> N |
Takes a root string, a singular pattern string, a broken plural pattern string, a gender, and species. Gives a noun. (This is also overloaded as mkN.) |
sdfN |
(root,sgPat : Str) -> Gender -> Species -> N |
Takes a root string, a singular pattern string, a gender, and species. Gives a noun whose plural is sound feminine. |
sdmN |
(root,sgPat : Str) -> Gender -> Species -> N |
Takes a root string, a singular pattern string, a gender, and species. Gives a noun whose plural is sound masculine |
dualN |
N -> N |
Force the plural of the N into dual (e.g. "twins") |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
Predictable PN from a Str: fem hum if ends in ة, otherwise masc hum. |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
Make a PN out of N. The PN is in construct state. |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> Species -> PN |
Make a PN out of string, gender and species. |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
Noun and a ready-made preposition. |
mkN2 |
N -> Str -> N2 |
Noun, preposition given as a string, complement case genitive. |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
Noun, no preposition, complement case genitive. |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
Predictable inflection, no preposition, complement case genitive. |
mkN3 |
N -> Preposition -> Preposition -> N3 |
ready-made prepositions |
mkN3 |
N -> Str -> Str -> N3 |
prepositions given as strings |
mkA |
(root : Str) -> A |
adjective with positive form aFCal |
mkA |
(root,sgPat : Str) -> A |
adjective with sound plural, takes root string and sg. pattern string |
mkA |
(root,sgPat,plPat : Str) -> A |
adjective with broken plural, same for both fem. and masc. |
mkA |
(isSoundFem : Bool) -> (root,sg,pl : Str) -> A |
adjective with broken plural, boolean argument whether feminine is sound (True) or shared with masc (False) |
mkA |
A -> Str -> A |
add non-inflecting component after adjective |
mkA |
Str -> A -> A |
add non-inflecting component before adjective |
nisbaA |
Str -> Adj |
Forms relative adjectives with the suffix ِيّ. Takes either the stem and adds يّ, or the whole word ending in يّ and just adds declension. |
idaafaA |
N -> A -> A |
Forms adjectives of type غَيْرُ طَيِّبٍ 'not good'. Noun is in construct state but inflects in case. Adjective is in genitive, but inflects in gender, number and state. |
degrA |
(masc,fem,plur : Str) -> A |
Adjective where masculine singular is also the comparative form. Indeclinable singular, basic triptote declension for dual and plural. |
irregFemA |
(masc : A) -> (fem : A) -> A |
Adjective with irregular feminine. Takes two adjectives (masc. regular and fem. "regular", with fem. forms in the masc fields,) and puts them together. |
invarGenderA |
A -> A |
Forms an adjective that has no feminine form. Takes a regular adjective and forces the masculine forms into the fem. table. |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
mkSubj |
Str -> Subj |
Default order Subord (=noun first and in accusative) |
mkSubj |
Str -> Order -> Subj |
Specify word order |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
Build a preposition out of the given string, with genitive case. |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
Build a preposition out of the given string and case. |
mkPrep |
Case -> Prep |
Just a case, no preposition. |
liPrep |
Prep | The preposition لِ, binding to its head. Vowel assimilation and def. article elision implemented. |
biPrep |
Prep | The preposition بِ, binding to its head. |
noPrep |
Prep | No preposition at all, "complement case" is nominative. |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
either … or |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
and, pl |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either, or, sg |
mkV |
(imperfect,masdar : Str) -> V |
Takes a verb of Form I in 3rd person masculine imperfect tense. Unpredictable masdar given as an argument. |
mkV |
(imperfect : Str) -> V |
Takes a verb of Form I in 3rd person masculine imperfect tense. Dummy masdar inserted. |
mkV |
(root : Str) -> (perf,impf : Vowel) -> (masdar : Str) -> V |
Takes the root of a verb of Form I. Vowel is one of {va,vi,vu}. Unpredictable masdar given as an argument. |
mkV |
(root : Str) -> (perf,impf : Vowel) -> V |
Like above, but dummy masdar inserted. This function is here only to keep compatibility for the old API; for new grammars, use the constructor with masdar as an argument. |
mkV |
(root,masdar : Str) -> VerbForm -> V |
FormI…FormXI (no IX). XI is quadriliteral. For FormI, default vowels are va and vu. The given masdar is used for FormI, but currently ignored for Forms II-XI. |
mkV |
(root : Str) -> VerbForm -> V |
Like above, but dummy masdar inserted for FormI verbs. No difference for FormII-FormXI, because they have predictable masdar. |
mkV |
V -> (particle : Str) -> V |
V with a non-inflecting particle/phrasal verb |
reflV |
V -> V |
نَفْس in the proper case and with possessive suffix, e.g. نَفْسَكِ |
v1 |
(root : Str) -> (perf,impf : Vowel) -> (masdar : Str) -> V |
Verb Form I: fa`ala, fa`ila, fa`ula. Verbal noun (masdar) given as the third argument. |
v1 |
(root : Str) -> (perf,impf : Vowel) -> V |
To keep compatibility for the old API; dummy masdar inserted. |
v2 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form II: fa``ala |
v3 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form III: faa`ala |
v4 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form IV: 'af`ala |
v5 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form V: tafa``ala |
v6 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form VI: tafaa`ala |
v7 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form VII: infa`ala |
v8 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form VIII: ifta`ala |
v10 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form X: 'istaf`ala |
v11 |
Str -> V |
Verb Form XI (quadriliteral): fa`laba |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
No preposition |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
Preposition as string, default case genitive |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
Ready-made preposition |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
Predictable verb conjugation, no preposition |
dirV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
speak, with, about |
mkV3 |
V -> (to : Str) -> (about:Str) -> V3 |
like above, but with strings as arguments (default complement case genitive) |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
give,_,to |
dirV3 |
V -> (to : Str) -> V3 |
like above, but with string as argument (default complement case genitive) |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
give,_,_ |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
Takes a V, returns a VS with default complementiser أَنَّ. |
mkVS |
V -> Str -> VS |
Takes a V and a complementiser. |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
Takes a V, returns a V2S with default complementiser أَنَّ and accusative as the direct object case. |
mkV2S |
VS -> V2S |
Takes a VS, returns a V2S with accusative as the object case, retaining the VS's complementiser. |
mkV2S |
V2 -> V2S |
Takes a V2, returns a V2S with default complementiser أَنَّ, retaining the V2's direct object case. |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> Str -> V2S |
Takes V, preposition and complementiser. |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
Takes a V, returns a VV with default complementiser أَنَّ. |
mkVV |
V -> Str -> VV |
Takes a V and a complementiser. |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
Takes a V, returns a V2V with default complementiser أَنْ and accusative as the direct object case. |
mkV2V |
VV -> V2V |
Takes VV, returns V2V with accusative as the object case, retaining the VV's complementiser. |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Str -> V2V |
Takes V, preposition and complementiser. |
subjCase |
VV -> Prep -> VV |
Change the subject case of a VV. (Default is nominative; use any other case or preposition.) |
subjCase |
V2V -> Prep -> V2V |
Change the subject case to a V2V. (Default is nominative; use any other case or preposition.) |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Str -> V2A |
Takes a V and an object case/preposition. NB. V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Str -> V2Q |
Takes a V and an object case/preposition. NB. V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
- |
mkA2S |
A -> Str -> A2S |
- |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
- |
mkA2V |
A -> Str -> A2V |
- |
V0 |
Type | - |
Paradigms for Bulgarian
source ../../src/bulgarian/ParadigmsBul.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
mkN001 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN001a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN002 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN002a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN003 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN004 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN005 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN006 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN007 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN007b |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN007a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN008 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN008b |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN008c |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN008a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN009 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN009a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN010 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN011 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN012 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN013 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN014 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN014a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN015 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN015a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN016 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN016a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN017 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN018 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN018a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN019 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN019a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN020 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN021 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN022 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN023 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN024a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN024 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN025 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN026 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN027 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN028 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN028a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN029 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN030 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN031 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN031a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN032 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN032a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN033 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN034 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN035 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN035a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN036 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN037 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN038 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN039 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN040 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN040a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN041 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN041a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN041b |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN042 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN043 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN043a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN044 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN045 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN046 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN047 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN048 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN049 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN050 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN051 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN052 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN052a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN053 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN054 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN055 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN056 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN057 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN057a |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN058 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN059 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN060 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN061 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN062 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN063 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN064 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN065 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN066 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN067 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN068 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN069 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN070 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN071 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN072 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN073 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN074 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN075 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN076 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN077 |
Str -> N |
- |
mkA076 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA077 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA078 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA079 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA080 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA081 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA082 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA082a |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA083 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA084 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA084a |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA085 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA086 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA087 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA088 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA089a |
Str -> A |
- |
mkV142 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV143 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV144 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV145 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV145a |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV145b |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV146 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV146a |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV147 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV148 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV149 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV150 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV150a |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV151 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV152 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV152a |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV153 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV154 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV155 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV156 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV157 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV158 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV159 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV160 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV160a |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV161 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV161a |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV162 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV163 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV164 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV165 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV166 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV167 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV168 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV169 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV170 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV171 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV172 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV173 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV174 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV175 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV176 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV177 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV178 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV179 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV180 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV181 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV182 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV183 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV184 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV185 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV186 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV187 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
mkV188 |
Str -> VTable |
- |
adjAdv |
A -> Str -> A |
- |
Paradigms for Catalan
source ../../src/catalan/ParadigmsCat.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
accusative |
Prep | direct object |
genitive |
Prep | preposition "de" |
dative |
Prep | preposition "a" |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
other preposition |
CopulaType |
Type | - |
serCopula |
CopulaType | - |
estarCopula |
CopulaType | - |
mkN |
(llum : Str) -> N |
regular, with heuristics for plural and gender |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
force gender |
mkN |
(disc,discos : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case |
compN |
N -> Str -> N |
compound, e.g. "número" + "de telèfon" |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. filla + genitive |
deN2 |
N -> N2 |
relation with genitive |
aN2 |
N -> N2 |
relation with dative |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. connexió + genitive + dative |
mkPN |
(Anna : Str) -> PN |
feminine for "-a", otherwise masculine |
mkPN |
(Pilar : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
force gender |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
- |
mkA |
(sol : Str) -> A |
regular |
mkA |
(fort,forta,forts,fortes,fortament : Str) -> A |
worst case |
mkA |
(bo : A) -> (millor : A) -> A |
special comparison (default with "mas") |
mkA |
A -> CopulaType -> A |
force copula type |
prefixA |
A -> A |
adjective before noun (default: after) |
adjCopula |
A -> CopulaType -> A |
force copula type |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. "casat" + dative |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkV |
(cantar : Str) -> V |
regular in models I, IIa, IIb |
mkV |
(servir,serveixo : Str) -> V --inchoative verbs and "re" verbs whose 1st person ends in c |
- |
mkV |
Verbum -> V |
use verb constructed in BeschCat |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
particle verb |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive verb |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
regular verb, direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
any verb, direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
preposition for complement |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
parlar, a, de |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
donar,(accusative),a |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
donar,(dative),(accusative) |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
subjVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
plain infinitive: "vull parlar" |
deVV |
V -> VV |
"acabar de parlar" |
aVV |
V -> VV |
"aprendre a parlar" |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for Chinese (simplified)
source ../../src/chinese/ParadigmsChi.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
mkN |
(man : Str) -> N |
- |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> Str -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkPN |
(john : Str) -> PN |
- |
foreignPN |
(john : Str) -> PN |
- |
mkA |
(small : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(small : Str) -> Bool -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
Str -> A2 |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> A2 |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
(walk : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(walk,out : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(arrive : Str) -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> V |
- |
mkV |
(arrive : Str) -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkVV |
Str -> VV |
- |
mkVQ |
Str -> VQ |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkVS |
Str -> VS |
- |
mkVS |
Str -> Str -> VS |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVA |
Str -> VA |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2Q |
Str -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2V |
Str -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
Str -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2A |
Str -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> AdvType -> Adv |
- |
mkAdv |
Adv -> AdvType -> Adv |
To fix the AdvType in an Adv produced by SyntaxChi.mkAdv |
AdvType |
Type | - |
placeAdvType |
AdvType | without "在" included |
zai_placeAdvType |
AdvType | with "在" included |
timeAdvType |
AdvType | - |
mannerAdvType |
AdvType | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Str -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Str -> AdvType -> Prep |
- |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
emptyPrep |
Preposition | - |
mkpNP |
Str -> CatChi.NP |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkSubj |
Str -> Subj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
(both,and : Str) -> Conj |
- |
mkpDet |
Str -> Det |
- |
mkQuant |
Str -> Quant |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkNum |
Str -> Num |
- |
mkPredet |
Str -> Predet |
- |
mkIDet |
Str -> IDet |
- |
mkPConj |
Str -> PConj |
- |
mkRP |
Str -> RP |
- |
Paradigms for Czech
source ../../src/czech/ParadigmsCze.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mascAnimate |
Gender | - |
mascInanimate |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neuter |
Gender | - |
nominative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
vocative |
Case | - |
locative |
Case | - |
instrumental |
Case | - |
mkN |
(nom : Str) -> N |
- |
mkN |
(nom,gen : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
panN |
Str -> N |
default ** {pnom |
predsedaN |
Str -> N |
default ** {sgen |
hradN |
Str -> N |
default ** {sgen,sloc |
zenaN |
Str -> N |
default ** {pgen |
mestoN |
Str -> N |
default ** {sloc |
muzN |
Str -> N |
- |
soudceN |
Str -> N |
default ** {sdat,sloc |
strojN |
Str -> N |
- |
ruzeN |
Str -> N |
- |
pisenN |
Str -> N |
- |
kostN |
Str -> N |
- |
kureN |
Str -> N |
- |
moreN |
Str -> N |
default ** {pgen |
staveniN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
- |
mladyA |
Str -> A |
- |
jarniA |
Str -> A |
- |
otcuvA |
Str -> A |
- |
matcinA |
Str -> A |
- |
invarA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkV2 |
VerbForms -> VerbForms ** {c : ComplementCase} |
- |
mkV2 |
VerbForms -> Case -> VerbForms ** {c : ComplementCase} |
- |
mkV2 |
VerbForms -> ComplementCase -> VerbForms ** {c : ComplementCase} |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
Paradigms for Danish
source ../../src/danish/ParadigmsDan.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
utrum |
Gender | "en" gender |
neutrum |
Gender | "et" gender |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
e.g. "til" |
noPrep |
Prep | empty string |
mkN |
(bil : Str) -> N |
regular noun: "en" gender with plural "-er" or "-r" |
mkN |
(bil,bilen : Str) -> N |
prediction from both singular indefinite and definite |
mkN |
(bil,biler : Str) -> Gender -> N |
prediction from both singular and plural plus gender |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenge,drengene : Str) -> N |
almost worst case, gender guessed from Sg Def |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenge,drengene : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. datter + til |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. forbindelse + fra + til |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
utrum gender |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
other gender |
mkA |
(fin : Str) -> A |
regular adjective |
mkA |
(fin,fint : Str) -> A |
deviant neuter |
mkA |
(galen,galet,galne : Str) -> A |
also deviant plural |
mkA |
(stor,stort,store,storre,storst : Str) -> A |
worst case |
mkA |
A -> A |
force comparison with mer/mest |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. gift + med |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
after verb, e.g. "idag" |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
close to verb, e.g. "altid" |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
modify adjective, e.g. "meget" |
mkV |
(snakke : Str) -> V |
regular verb |
mkV |
(leve,levde : Str) -> V |
also give past tense |
mkV |
(drikke, drakk, drukket : Str) -> V |
theme of irregular verb |
mkV |
(spise,spiser,spises,spiste,spist,spis : Str) -> V |
worst case |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
particle verb, e.g. lukke + op |
vaereV |
V -> V |
force auxiliary "være" |
depV |
V -> V |
deponent, e.g. "undres" |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive, e.g. "forestille sig" |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
prepositional object |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
snakke, med, om |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
give,_,til |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
give,_,_ |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for Dutch
source ../../src/dutch/ParadigmsDut.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
de |
Gender | non-neutrum |
het |
Gender | neutrum |
nominative |
Case | nominative of nouns |
genitive |
Case | genitive of nouns |
mkN |
(bank : Str) -> N |
de bank-banken, with some predictable exceptions |
mkN |
(bit : Str) -> Gender -> N |
if gender is not predictable |
mkN |
(gat, gaten : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst-case for nouns |
mkN |
(werk, plaats : N) -> N |
compound werkplaats |
mkN |
(station, hal : N) -> Case -> N |
compound stationshal |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition van |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
other preposition than van |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. afstand + van + naar |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
proper name |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
proper name from noun |
mkA |
(vers : Str) -> A |
regular adjective |
mkA |
(tweed,tweede : Str) -> A |
with deviant second form |
mkA |
(goed,goede,goeds,beter,best : Str) -> A |
irregular adjective |
invarA |
Str -> A |
adjective with just one form |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. getrouwd + met |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
van_Prep |
Prep | - |
te_Prep |
Prep | - |
mkV |
(aaien : Str) -> V |
regular verb |
mkV |
(aaien,aait : Str) -> V |
regular verb with third person sg pres (giving stem) |
mkV |
(breken,brak,gebroken : Str) -> V |
theme of irregular verb |
mkV |
(breken,brak,braken,gebroken : Str) -> V |
also past plural irregular |
mkV |
(aai,aait,aaien,aaide,aaide,aaiden,geaaid : Str) -> V |
almost worst-case verb, Sg2=Sg3 |
mkV |
(aai,aait,aait,aaien,aaide,aaide,aaiden,geaaid : Str) -> V |
worst-case verb |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
add movable suffix, e.g. af + stappen |
no_geV |
V -> V |
no participle "ge", e.g. "vertrekken" |
fixprefixV |
Str -> V -> V |
add prefix such as "be"; implies no_ge |
zijnV |
V -> V |
force zijn as auxiliary (default hebben) |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive verb e.g. zich afvragen |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
geven,(accusative),(dative) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
sturen,(accusative),naar |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
praten, met, over |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
with "te" |
auxVV |
V -> VV |
without "te" |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
auxV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
auxV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> V2Q |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
Paradigms for English
source ../../src/english/ParadigmsEng.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
human |
Gender | - |
nonhuman |
Gender | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
npNumber |
NP -> Number |
exctract the number of a noun phrase |
mkN |
(flash : Str) -> N |
plural s, incl. flash-flashes, fly-flies |
mkN |
(man,men : Str) -> N |
irregular plural |
mkN |
(man,men,man's,men's : Str) -> N |
irregular genitives |
mkN |
Gender -> N -> N |
default nonhuman |
mkN |
Str -> N -> N |
e.g. baby + boom |
verbalN |
V -> N |
e.g. sing -> singing |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
e.g. wife of (default prep. to) |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. access to |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. connection from x to y |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkA |
(happy : Str) -> A |
regular adj, incl. happy-happier, rude-ruder |
mkA |
(fat,fatter : Str) -> A |
irreg. comparative |
mkA |
(good,better,best,well : Str) -> A |
completely irreg. |
compoundA |
A -> A |
force comparison with more/most |
simpleA |
A -> A |
force comparison with -er,-est |
irregAdv |
A -> Str -> A |
adverb irreg, e.g. "fast" |
invarA |
Str -> A |
adjective that does not vary in morphology |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
absent from |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
e.g. today |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
e.g. always |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
e.g. quite |
mkCAdv |
Str -> Str -> Str -> CAdv |
more than/no more than |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
e.g. approximately |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
e.g. "in front of" |
mkPost |
Str -> Prep |
e.g. "ago" |
noPrep |
Prep | no preposition |
mkV |
(cry : Str) -> V |
regular, incl. cry-cries, kiss-kisses etc |
mkV |
(stop, stopped : Str) -> V |
reg. with consonant duplication |
mkV |
(drink, drank, drunk : Str) -> V |
ordinary irregular |
mkV |
(go, goes, went, gone, going : Str) -> V |
totally irregular |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
fix compound, e.g. under+take |
partV |
V -> Str -> V |
with particle, e.g. switch + on |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive e.g. behave oneself |
us_britishV |
Str -> V |
travel - traveled/travelled |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
transitive, e.g. hit |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
with preposiiton, e.g. believe in |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
ditransitive, e.g. give,_,_ |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
two prepositions, e.g. speak, with, about |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
sentence-compl e.g. say (that S) |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
e.g. tell (NP) (that S) |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
e.g. want (to VP) |
auxVV |
V -> VV |
e.g. must (VP) |
infVV |
V -> VV |
e.g. must (VP) (old name of auxVV) |
ingVV |
V -> VV |
e.g. start (VPing) |
mkV2V |
Str -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
e.g. want (noPrep NP) (to VP) |
ingV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
e.g. prevent (noPrep NP) (from VP-ing) |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
e.g. become (AP) |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
e.g. paint (NP) (AP) |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
backwards compatibility |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
e.g. strike (NP) as (AP) |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
e.g. wonder (QS) |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
e.g. ask (NP) (QS) |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
Paradigms for Estonian
source ../../src/estonian/ParadigmsEst.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
Case |
Type | - |
nominative |
Case | e.g. "karp" |
genitive |
Case | e.g. "karbi" |
partitive |
Case | e.g. "karpi" |
illative |
Case | e.g. "karbisse/karpi" |
inessive |
Case | e.g. "karbis" |
elative |
Case | e.g. "karbist" |
allative |
Case | e.g. "karbile" |
adessive |
Case | e.g. "karbil" |
ablative |
Case | e.g. "karbilt" |
translative |
Case | e.g. "karbiks" |
terminative |
Case | e.g. "karbini" |
essive |
Case | e.g. "karbina" |
abessive |
Case | e.g. "karbita" |
comitative |
Case | e.g. "karbiga" |
infDa |
InfForm | e.g. "lugeda" |
infDes |
InfForm | e.g. "lugedes" |
infMa |
InfForm | e.g. "lugema" |
infMas |
InfForm | e.g. "lugemas" |
infMaks |
InfForm | e.g. "lugemaks" |
infMast |
InfForm | e.g. "lugemast" |
infMata |
InfForm | e.g. "lugemata" |
prePrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
preposition, e.g. abessive "ilma" |
postPrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
postposition, e.g. genitive "taga" |
postGenPrep |
Str -> Prep |
genitive postposition, e.g. "taga" |
casePrep |
Case -> Prep |
just case, e.g. adessive |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
just one word, default number Sg: e.g. "ja" |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj --just one word + number: e.g. "ja" Pl |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj --two words, default number: e.g. "nii" "kui" |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj --two words + number: e.g. "nii" "kui" Pl |
- |
mkPConj |
Str -> PConj |
- |
mkN |
(ema : Str) -> N |
predictable nouns, covers 90% |
mkN |
(tukk,tuku : Str) -> N |
sg nom,gen: unpredictable stem vowel |
mkN |
(tukk,tuku,tukku : Str) -> N |
sg nom,gen,part |
mkN |
(pank,panga,panka,panku : Str) -> N |
sg nom,gen,part, pl.part |
mkN |
(oun,ouna,ouna,ounasse,ounte,ounu : Str) -> N |
worst case, 6 forms |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with genitive |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
relational noun another prep. |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
relation with two complements |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
predictable noun made into name |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
any noun made into name |
mkA |
Str -> A |
regular noun made into adjective |
mkA |
N -> A |
any noun made into adjective |
mkA |
N -> (infl : Infl) -> A |
noun made into adjective, agreement type specified |
mkA |
N -> (parem, parim : Str) -> A |
deviating comparison forms |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. "vihane" (postGenPrep "peale") |
invA |
Str -> A |
invariable adjectives, such as genitive attributes ; no agreement to head, no comparison forms. |
mkV |
(lugema : Str) -> V |
predictable verbs, covers 90 % |
mkV |
(lugema,lugeda : Str) -> V |
ma infinitive, da infinitive |
mkV |
(lugema,lugeda,loeb : Str) -> V |
ma, da, present sg 3 |
mkV |
(lugema,lugeda,loeb,loetakse : Str) -> V --ma, da, pres sg 3, pres passive |
- |
mkV |
(tegema,teha,teeb,tehakse,tehke,tegi,teinud,tehtud : Str) -> V |
worst-case verb, 8 forms |
mkV |
(saama : V) -> (aru : Str) -> V |
multi-word verbs |
caseV |
Case -> V -> V |
deviating subj. case, e.g. allative "meeldima" |
vOlema |
V | the verb "be" |
vMinema |
V | the verb "go" |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
predictable direct transitive |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct transitive |
mkV2 |
V -> Case -> V2 |
complement just case |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
complement pre/postposition |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
e.g. rääkima, allative, elative |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
string, default cases accusative + allative |
dirV3 |
V -> Case -> V3 |
liigutama, (accusative), illative |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
andma, (accusative), (allative) |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVS |
Str -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
e.g. "ütlema" allative |
mkV2S |
Str -> V2S --default (mkV foo) allative |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
e.g. "hakkama" |
mkVV |
Str -> VV |
- |
mkVVf |
V -> InfForm -> VV |
e.g. "hakkama" infMa |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
e.g. "käskima" adessive |
mkV2V |
Str -> V2V |
e.g. "käskima" adessive |
mkV2Vf |
V -> Prep -> InfForm -> V2V |
e.g. "keelama" partitive infMast |
mkVA |
V -> Prep -> VA |
e.g. "muutuma" translative |
mkVA |
Str -> VA |
string, default case translative |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
e.g. "värvima" genitive translative |
mkV2A |
Str -> V2A |
string, default cases genitive and translative |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkVQ |
Str -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
e.g. "küsima" ablative |
Paradigms for Basque
source ../../src/basque/ParadigmsEus.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Number |
Type | - |
sg |
Number | - |
pl |
Number | - |
AuxType |
Type | - |
da |
AuxType | - |
du |
AuxType | - |
zaio |
AuxType | - |
dio |
AuxType | - |
Case |
Type | - |
absolutive |
Case | - |
ergative |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
partitive |
Case | - |
inessive |
Case | - |
instrumental |
Case | Instrumental : |
sociative |
Case | Sociative/comitative : txakurrarekin `with the dog' |
Animacy |
Type | - |
animate |
Animacy | - |
inanim |
Animacy | - |
mkN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN |
Str -> Bizi -> N |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
Str -> Case -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Case -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
Str -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
Str -> Case -> Case -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
Str -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Case -> Case -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
Str -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> AuxType -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkVA |
Str -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
Str -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
Str -> VQ |
- |
mkVS |
Str -> VS |
- |
mkV2V |
Str -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
Str -> V2S |
- |
mkV2Q |
Str -> V2Q |
- |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
- |
izanV |
Str -> Verb |
- |
egonV |
Str -> Verb |
- |
ukanV |
Str -> Verb |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> (complCase : Case) -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> (complCase : Case) -> (affixed : Bool) -> Prep |
- |
affixPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
- |
locPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkConj |
(_,_ : Str) -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkSubj |
Str -> Bool -> Subj |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
Paradigms for Finnish
source ../../src/finnish/ParadigmsFin.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
Case |
Type | - |
nominative |
Case | e.g. "talo" |
genitive |
Case | e.g. "talon" |
partitive |
Case | e.g. "taloa" |
essive |
Case | e.g. "talona" |
translative |
Case | e.g. "taloksi" |
inessive |
Case | e.g. "talossa" |
elative |
Case | e.g. "talosta" |
illative |
Case | e.g. "taloon" |
adessive |
Case | e.g. "talolla" |
ablative |
Case | e.g. "talolta" |
allative |
Case | e.g. "talolle" |
infFirst |
InfForm | e.g. "tehdä" |
infIness |
InfForm | e.g. "tekemässä" |
infElat |
InfForm | e.g. "tekemästä" |
infIllat |
InfForm | e.g. "tekemään" |
infAdess |
InfForm | e.g. "tekemällä" |
infPart |
InfForm | e.g. "tekemistä" |
infPresPart |
InfForm | e.g. "tekevän" |
infPresPartAgr |
InfForm | e.g. "tekevänsä" |
prePrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
preposition, e.g. partitive "ilman" |
postPrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
postposition, e.g. genitive "takana" |
postGenPrep |
Str -> Prep |
genitive postposition, e.g. "takana" |
casePrep |
Case -> Prep |
just case, e.g. adessive |
mkPrep |
Case -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
- |
accusative |
Prep | - |
NK |
Type | Noun from DictFin (Kotus) |
AK |
Type | Adjective from DictFin (Kotus) |
VK |
Type | Verb from DictFin (Kotus) |
AdvK |
Type | Adverb from DictFin (Kotus) |
mkN |
(kukko : Str) -> N |
predictable nouns, covers 82% |
mkN |
(savi,savia : Str) -> N |
different pl.part |
mkN |
(vesi,veden,vesiä : Str) -> N |
also different sg.gen |
mkN |
(vesi,veden,vesiä,vettä : Str) -> N |
also different sg.part |
mkN |
(olo,n,a,na,oon,jen,ja,ina,issa,ihin : Str) -> N |
worst case, 10 forms |
mkN |
(pika : Str) -> (juna : N) -> N |
compound with invariable prefix |
mkN |
(oma : N) -> (tunto : N) -> N |
compound with inflecting prefix |
mkN |
NK -> N |
noun from DictFin (Kotus) |
mkN |
V -> N |
verbal noun: "tekeminen" |
verbalN |
V -> N |
tekeminen |
exceptNomN |
N -> Str -> N |
- |
separateN |
Str -> N -> N |
- |
separateN |
N -> N -> N |
- |
compN |
N -> N -> N |
- |
genCompN |
N -> N -> N |
- |
genCompN |
Number -> N -> N -> N |
- |
genitiveCompoundN |
Number -> N -> N -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with genitive |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
relational noun another prep. |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
relation with two complements |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
predictable noun made into name |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
any noun made into name |
foreignPN |
Str -> PN |
Dieppe-Dieppen |
mkA |
Str -> A |
regular noun made into adjective |
mkA |
N -> A |
any noun made into adjective |
mkA |
N -> (kivempi,kivin : Str) -> A |
deviating comparison forms |
mkA |
(hyva,prmpi,pras : N) -> (hyvin,pmmin,prhten : Str) -> A |
worst case adj |
mkA |
AK -> A |
adjective from DictFin (Kotus) |
invarA |
Str -> A |
invariant adjective, e.g. "kelpo" |
compoundA |
Str -> A -> A |
prefix glued to adjective, e.g. "hevos"+"vetoinen" |
prefixA |
Str -> A -> A |
in modifying use, an uninflected glued prefix, e.g. "sähkö" for "sähköinen" |
mkA2 |
Str -> A2 |
e.g. "vihainen" (jollekin) |
mkA2 |
Str -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. "jaollinen" (mkPrep adessive) |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. "jaollinen" (mkPrep adessive) |
mkV |
(huutaa : Str) -> V |
predictable verbs, covers 90% |
mkV |
(huutaa,huusi : Str) -> V |
deviating past 3sg |
mkV |
(huutaa,huudan,huusi : Str) -> V |
also deviating pres. 1sg |
mkV |
(huutaa,dan,taa,tavat,takaa,detaan,sin,si,sisi,tanut,dettu,tanee : Str) -> V |
worst-case verb |
mkV |
VK -> V |
verb from DictFin (Kotus) |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
hakata päälle (particle verb) |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
laimin+lyödä (prefixed verb) |
caseV |
Case -> V -> V |
deviating subj. case, e.g. genitive "täytyä" |
vOlla |
V | the verb "be" |
olla_V |
V | - |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
predictable direct transitive |
mkV2 |
Str -> Case -> V2 |
predictable with another case |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct transitive |
mkV2 |
V -> Case -> V2 |
complement just case |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
complement pre/postposition |
mkV2 |
VK -> V2 |
direct transitive of Kotus verb |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
e.g. puhua, allative, elative |
dirV3 |
V -> Case -> V3 |
siirtää, (accusative), illative |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
antaa, (accusative), (allative) |
mkVV |
Str -> VV |
e.g. "yrittää" (puhua) |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
e.g. "alkaa" (puhua) |
mkVV |
Str -> InfForm -> VV |
e.g. "ruveta" (puhumaan) |
mkVV |
V -> InfForm -> VV |
e.g. "lakata" (puhumasta) |
mkVS |
Str -> VS |
e.g. "väittää" |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
e.g. "sanoa" |
mkV2V |
Str -> V2V |
reg verb, partitive + infIllat |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
partitive + infillat |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
e.g. "käskeä" genitive + infFiilat |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> InfForm -> V2V |
e.g. "kieltää" partitive infElat |
mkV2V |
V -> Case -> InfForm -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
e.g. "sanoa" allative |
mkVVf |
V -> InfForm -> VV |
e.g. "ruveta" infIllat |
mkV2Vf |
V -> Prep -> InfForm -> V2V |
e.g. "kieltää" partitive infElat |
mkVA |
V -> Prep -> VA |
e.g. "maistua" ablative |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
e.g. "maalata" accusative translative |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
e.g. "kysyä" ablative |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkPConj |
Str -> PConj |
- |
mkSubj |
Str -> Subj |
- |
mkPredet |
Str -> Predet |
invariable Predet, such as "vain" |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkDet |
Number -> N -> Det |
- |
mkDet |
(isNeg : Bool) -> Number -> N -> Det |
use this with True to create a negative determiner |
mkDet |
(isNeg : Bool) -> Number -> N -> Case -> Det |
paljon + False + partitive, ei yhtään + True + partitive |
mkQuant |
N -> Quant |
- |
mkQuant |
N -> N -> Quant |
- |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
Paradigms for French
source ../../src/french/ParadigmsFre.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
accusative |
Prep | direct object case |
genitive |
Prep | genitive, constructed with "de" |
dative |
Prep | dative, usually constructed with "à" |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
simple preposition (other than "de" and "à") |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep -> Prep |
complex preposition e.g. "à côté de" |
mkN |
(cheval : Str) -> N |
predictable, with variations like cheval-chevaux |
mkN |
(oeil,yeux : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst-case noun |
mkN |
N -> Str -> N |
compound noun, e.g. numéro + de téléphone |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. fille + genitive |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. connection + genitive + dative |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
feminine if ends with "e", otherwise masculine |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
gender deviant from the simple rule |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
gender inherited from noun |
mkA |
(cher : Str) -> A |
predictable, e.g. cher-chère |
mkA |
(sec,seche : Str) -> A |
unpredictable feminine |
mkA |
(banal,banale,banaux : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(banal,banale,banaux,banalement : Str) -> A |
almost worst-case adjective |
mkA |
(vieux,vieil,vieille,vieuxs,vieuxment : Str) -> A |
worst-case adjetive |
mkA |
A -> A -> A |
irregular comparison, e.g. bon-meilleur |
mkA |
A -> CopulaType -> A |
force copula type |
prefixA |
A -> A |
adjective that comes before noun, e.g. petit |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. supérieur + dative |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
ordinary adverb |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
sentential adverb, e.g. toujours |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
modify adjective, e.g. très |
mkV |
(finir : Str) -> V |
regular 1/2/3 conjugation |
mkV |
(jeter,jette : Str) -> V |
1st and 2nd conjugation variations |
mkV |
(jeter,jette,jettera : Str) -> V |
1st conjugation variations |
mkV |
(tenir,tiens,tenons,tiennent,tint,tiendra,tenu : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(tenir,tiens,tient,tenons,tenez,tiennent,tienne,tenions,tiensI,tint,tiendra,tenu : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
V2 -> V |
make 2-place to 1-place (e.g. from IrregFre) |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
- |
etreV |
V -> V |
force auxiliary to be être (default avoir) |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive, implies auxiliary être, e.g. se demander |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct transitive |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
e.g. se fier + genitive |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
donner (+ accusative + dative) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
placer (+ accusative) + dans |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
parler + dative + genitive |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
subjVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
plain infinitive: "je veux parler" |
deVV |
V -> VV |
"j'essaie de parler" |
aVV |
V -> VV |
"j'arrive à parler" |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for German
source ../../src/german/ParadigmsGer.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neuter |
Gender | - |
Case |
Type | - |
nominative |
Case | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
vonDat_Case |
Case | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mkN |
(Stufe : Str) -> N |
die Stufe-Stufen, der Tisch-Tische |
mkN |
(Bild,Bilder : Str) -> Gender -> N |
sg and pl nom, and gender |
mkN |
(Frau : Str) -> Gender -> N |
masc: e, neutr: er, fem: en |
mkN |
(x1,_,_,_,_,x6 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case: mann, mann, manne, mannes, männer, männern |
mkN |
Str -> N -> N |
Auto + Fahrer -> Autofahrer |
mkN |
N -> N -> N |
Freiheit + Kampf -> Freiheitskampf |
changeCompoundN |
Str -> N -> N |
kyrko + kyrka_N |
dative_eN |
N -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
noun + von |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
noun + other preposition |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
noun + two prepositions |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
regular name with genitive in "s", masculine |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
regular name with genitive in "s" |
mkPN |
(nom,gen : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
name with other genitive |
mkPN |
(nom,acc,dat,gen : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
name with all case forms |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
use the singular forms of a noun |
mkA |
Str -> A |
regular adjective, works for most cases |
mkA |
(gut,besser,beste : Str) -> A |
irregular comparison |
mkA |
(gut,gute,besser,beste : Str) -> A |
irregular positive if ending added |
invarA |
Str -> A |
invariable, e.g. prima |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. teilbar + durch |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
adverbs have just one form anyway |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
e.g. "durch" + accusative |
mkPrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
postposition |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Str -> Prep |
both sides |
accPrep |
Prep | no string, just accusative case |
datPrep |
Prep | no string, just dative case |
genPrep |
Prep | no string, just genitive case |
von_Prep |
Prep | von + dative |
zu_Prep |
Prep | zu + dative, with contractions zum, zur |
anDat_Prep |
Prep | an + dative, with contraction am |
inDat_Prep |
Prep | in + dative, with contraction ins |
inAcc_Prep |
Prep | in + accusative, with contraction im |
mkV |
(führen : Str) -> V |
regular verb |
mkV |
(sehen,sieht,sah,sähe,gesehen : Str) -> V |
irregular verb theme |
mkV |
(geben, gibt, gib, gab, gäbe, gegeben : Str) -> V |
worst-case verb |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
movable prefix, e.g. auf+fassen, or fix prefix if one of be,er,ge,ver,zer |
no_geV |
V -> V |
no participle "ge", e.g. "bedeuten" |
fixprefixV |
Str -> V -> V |
add prefix such as "be"; implies no_ge |
seinV |
V -> V |
force "sein" as auxiliary |
habenV |
V -> V |
force "haben" as auxiliary |
reflV |
V -> Case -> V |
reflexive, with case |
compoundV |
Str -> V -> V |
verb with a separate "particle", e.g. "Trinkgeld geben" |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
preposition for complement |
mkV2 |
V -> Case -> V2 |
just case for complement |
accdatV3 |
V -> V3 |
geben + dat(c2) + acc(c3) (Eng: no prepositions) |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
senden + acc + nach (preposition on second arg) |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
geben + dat(c3) + acc(c2) (Eng: give sth to-sb) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
sprechen + mit + über |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
auxV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
auxV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
subjV2V |
V2V -> V2V |
force subject-control |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
with zu |
auxVV |
V -> VV |
without zu |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkVA |
V -> Prep -> VA |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
Paradigms for Greek
source ../../src/greek/ParadigmsGre.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neutral |
Gender | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
indicative |
Mood | - |
conjunctive |
Mood | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mkN |
(dentro : Str) -> N |
- |
mkN |
(s : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(s1,s2,s3,s4,p1,p2,p3,p4 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(s1,s2: Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN1 |
Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkNending |
Str -> Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 ---η μητέρα + γενική |
- |
ofN2 |
N -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkPN |
(anna : Str) -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
(nm,gm,am,vm,pn,pa : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
- |
makeNP |
(_,_,_: Str) -> Number -> Gender -> NP |
- |
makeNP |
Str -> Number -> Gender ->Bool -> NP |
- |
mkpanta |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Gender -> NP |
- |
mkkati |
Str ->Number -> Gender -> Bool -> NP |
- |
mkA |
(a : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(a,b: Str) -> A |
- |
mkAd2 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkAd3 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkAd4 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkAd5 |
Str -> A |
- |
mkAdIrreg |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA1 |
Str -> Str -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> Prep -> A2V; |
- |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
- |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
acc |
Prep | - |
gen |
Prep | - |
dat |
Prep | - |
prepse |
Prep | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkPrep2 |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkPrep3 |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkPrep4 |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
Preposition |
Type | - |
mkPreposition |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkPreposition2 |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkPreposition3 |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkPreposition4 |
Str -> Preposition |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mmkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
milaw, se, gia |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
dino,_,se |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
dino,_,_ |
mmkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
dirV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
- |
V0 |
Type | - |
V0 |
Type | - |
mkNV |
Verb -> V |
- |
compoundV |
Verb -> Str -> V |
- |
Paradigms for Hindi
source ../../src/hindi/ParadigmsHin.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number; |
- |
plural |
Number; |
- |
mkN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(x1,_,_,_,_,x6 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> N2; |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> Str-> N3 |
- |
mkCmpdNoun |
Str -> N -> N |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
- |
personalPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Gender -> UPerson -> Pron |
- |
demoPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Quant |
- |
mkDet |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Det |
- |
mkIP |
(x1,x2,x3:Str) -> Number -> Gender -> IP |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkA |
Str-> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkA |
A -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkIrregA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> V3; |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Str -> Bool -> V2V |
- |
dirV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V -> V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V2 -> V |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Str -> Prep |
- |
mkIQuant |
(s1,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,s12:Str) -> IQuant |
- |
mkQuant |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkQuant |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and (plural agreement) |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
both ... and (plural) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either ... or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS; |
e.g drna |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
e.g janna |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
Paradigms for Icelandic
source ../../src/icelandic/ParadigmsIce.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neuter |
Gender | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
Case |
Type | - |
nominative |
Case | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
mkN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(_,_ : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(x1,_,_,_,_,_,_,x8 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkCompoundN |
Str -> N -> N |
- |
mkNPlGen |
Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mk0N |
Str -> N |
- |
mk1N |
Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mk2N |
(_,_ : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mk3N |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> Gender -> N =\x,y,z,g -> case g of { |
- |
mk4N |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> Gender -> N =\a,b,c,d,g -> case g of { |
- |
neutrNForms1 |
Str -> NForms |
- |
neutrNForms2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
neutrNForms3 |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
neutrNForms4 |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
mascNForms1 |
Str -> NForms |
- |
mascNForms2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
mascNForms3 |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> NForms =\nom,gen,pl -> case <nom,gen,pl> of { |
- |
mascNForms4 |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
femNForms1 |
Str -> NForms |
- |
femNForms2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
femNForms3 |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
femNForms4 |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> NForms |
- |
mk8N |
(x1,_,_,_,_,_,_,x8 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Preposition -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> (_,_ : Preposition) -> N3 |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA |
(_,_ : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> A |
- |
mk1A |
Str -> A |
- |
mk2A |
(_,_ : Str) -> A |
- |
mk3A |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> A |
- |
strongPosit1 |
Str -> AForms |
- |
strongPosit2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> AForms |
- |
weakPosit |
(_,_ : Str) -> AForms |
- |
compar1 |
Str -> AForms |
- |
compar2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> AForms |
- |
weakSuperl |
(_,_ : Str) -> AForms |
- |
strongSuperl1 |
Str -> AForms |
- |
strongSuperl2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> AForms |
- |
regAAdv1 |
Str -> Str |
- |
regAAdv2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> Str |
- |
addAdv |
A -> Str -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV |
(_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(_,_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(x1,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,x59 : Str) -> V |
- |
depV |
V -> V |
- |
mk1V |
Str -> V |
- |
mk2V |
(_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mk3V |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mk4V |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
mk5V |
(_,_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
indsub1 |
Str -> MForms |
- |
indsub2 |
(_,_ : Str) -> MForms |
- |
indsub3 |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> MForms |
- |
impSg |
Str -> Str |
- |
impPl |
Str -> Str |
- |
sup |
Str -> Str |
- |
presPart |
Str -> Str |
- |
strongPP |
Str -> AForms |
- |
weakPP |
Str -> AForms |
- |
irregV |
Str -> V |
- |
irregV |
(_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irregV |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irregV |
(_,_,_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irregV |
MForms -> (_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irreg1V |
Str -> V |
- |
irreg2V |
(_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irreg4V |
(_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irreg6V |
(_,_,_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
irreg9V |
MForms -> (_,_ : Str) -> V |
- |
impIrregSg |
Str -> Str |
- |
irregindsub |
Str -> MForms |
- |
irregindsub3 |
(_,_,_ : Str) -> MForms |
- |
irregindsub5 |
(_,_,_,_,_ : Str) -> MForms |
- |
prepV2 |
V -> Preposition -> V2 |
- |
prepV3 |
V -> Preposition -> Preposition -> V3 |
- |
accPrep |
Preposition | - |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Preposition -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
vowel |
pattern Str |
- |
consonant |
pattern Str |
- |
regPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkAdN |
CAdv -> AdN |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj =\y,n -> mk2Conj [] y n |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj =\x,y -> mk2Conj x y plural |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj =\x,y,n -> mk2Conj x y n |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
Paradigms for Italian
source ../../src/italian/ParadigmsIta.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
--Prep |
Type | - |
accusative |
Prep | direct object |
genitive |
Prep | preposition "di" and its contractions |
dative |
Prep | preposition "a" and its contractions |
di_Prep |
Prep | - |
a_Prep |
Prep | - |
con_Prep |
Prep | preposition "con" and its contractions |
da_Prep |
Prep | preposition "da" and its contractions |
in_Prep |
Prep | preposition "in" and its contractions |
su_Prep |
Prep | preposition "su" and its contractions |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
simple preposition (other than a, di, con, da, in, su) |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep -> Prep |
complex preposition e.g. "vicino a" |
mkN |
(cane : Str) -> N |
regular noun; fem for -"a", masc otherwise |
mkN |
(carne : Str) -> Gender -> N |
override default gender |
mkN |
(uomo,uomini : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case |
mkN |
N -> Str -> N |
compound such as "numero" + "di telefono" |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
regular with genitive, e.g. "figlio" + "di" |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
arbitrary noun and preposition |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. volo + da + per |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
femininne for "-a", otherwise masculine |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
set gender manually |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
get gender from noun |
mkA |
(bianco : Str) -> A |
predictable adjective |
mkA |
(solo,sola,soli,sole,solamente : Str) -> A |
irregular adjective |
mkA |
A -> A -> A |
special comparison, e.g. buono - migliore |
mkA |
A -> CopulaType -> A |
force copula type |
prefixA |
A -> A |
adjective that comes before noun (default: after) |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. divisibile + per |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
regular verbs in "-are"/"-ire" |
mkV |
Verbo -> V |
verbs formed by BeschIta |
mkV |
(udire,odo,ode,udiamo,udiro,udii,udisti,udi,udirono,odi,udito : Str) -> V |
worst case |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
particle verb |
essereV |
V -> V |
force "essere" as auxiliary (default avere) |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive verb (implies essere) |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
regular verb, direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
prepositional object |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
donner (+ accusative + dative) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
placer (+ accusative) + dans |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
parler + dative + genitive |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
dare,_,a |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
dare,_,_ |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
subjVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
plain infinitive: "voglio parlare" |
deVV |
V -> VV |
"cerco di parlare" |
aVV |
V -> VV |
"arrivo a parlare" |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkPredet |
Str -> Predet |
- |
Paradigms for Japanese
source ../../src/japanese/ParadigmsJpn.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
VerbGroup |
Type | Parameter for mkV* |
gr1 |
VerbGroup | Basic form ends in -u, consonant stem. |
gr2 |
VerbGroup | Basic form ends in -iru/-eru, vowel stem. |
suru |
VerbGroup | Irregular: kuru |
kuru |
VerbGroup | Irregular: suru |
Animacy |
Type | Parameter for mkN* |
animate |
Animacy | - |
inanimate |
Animacy | - |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> N |
Inanimate noun. Counter is つ and doesn't replace the noun. |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> N |
Animacy given as argument. Counter is つ and doesn't replace the noun. |
mkN |
(kane,okane : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> N |
Style variation (plain, respectful) and animacy given. Counter is つ and doesn't replace the noun. |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counter : Str) -> (counterReplace : Bool) -> N |
No style variation. Arguments are animacy, counter and whether counter replaces the noun. |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counterReplace : Bool) -> N |
No style variation. Arguments are animacy and whether counter replaces the noun (here the counter and the noun coincide, e.g. 'day' 日, 'two days' 二日, not 二日の日). |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counter : Str) -> N |
No style variation. Arguments are animacy and counter, which does not replace the noun. |
mkN |
(man : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counter : Str) -> (counterReplace : Bool) -> (men : Str) -> N |
Like previous, but unpredictable plural. |
mkN |
(kane,okane : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counter : Str) -> (counterReplace : Bool) -> N |
Plain form, respectful form, animacy, counter and whether counter replaces the noun. |
mkN |
(tsuma,okusan : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counter : Str) -> (counterReplace : Bool) -> (tsumatachi : Str) -> N |
Worst case paradigm: plain form, respectful form, animacy, counter, whether counter replaces the noun, and plural form. |
mkN2 |
(man : Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> (counter : Str) -> (counterReplace : Bool) -> (men : Str) -> (prep : Str) -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
(distance : Str) -> (prep1: Str) -> (prep2: Str) -> (anim : Animacy) -> N3 |
- |
mkPN |
(paris : Str) -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
(jon,jonsan : Str) -> PN |
- |
mkPron |
(kare : Str) -> (Pron1Sg : Bool) -> (anim : Animacy) -> Pron |
- |
mkPron |
(boku,watashi : Str) -> (Pron1Sg : Bool) -> (anim : Animacy) -> Pron |
- |
mkA |
(ookina : Str) -> A |
One form for both predicative and attribute |
mkA |
(kekkonshiteiru,kikonno : Str) -> A |
Verbal adjective, arguments are predicative and attributive |
mkA2 |
(yasui : Str) -> (prep : Str) -> A2 |
2-place adjective. Arguments: adjective (same for predicative and attributive) and object marker. |
mkA2 |
(pred : Str) -> (attr : Str) -> (prep : Str) -> A2 |
Predicative, attributive and object marker. |
mkV |
(yomu : Str) -> V |
Default: group 1 verb |
mkV |
(yomu : Str) -> (group : VerbGroup) -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
(yomu : Str) -> V2 |
Group 1 verb, を as object marker |
mkV2 |
(yomu, prep : Str) -> (group : VerbGroup) -> V2 |
Base form, object marker and verb group given |
mkV3 |
(yomu : Str) -> V3 |
Group 1 verb, に and を as object markers |
mkV3 |
(uru, p1, p2 : Str) -> (group : VerbGroup) -> V3 |
Base form, object markers and verb group given |
mkVS |
(yomu : Str) -> VS |
- |
mkVV |
(yomu : Str) -> VV |
- |
mkV2V |
(yomu : Str) -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
(yomu : Str) -> V2S |
- |
mkVQ |
(yomu : Str) -> VQ |
- |
mkVA |
(yomu : Str) -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
(yomu : Str) -> V2A |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkDet |
Str -> Det |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
mkgoVV |
VV | - |
Paradigms for Latin
source ../../src/latin/ParadigmsLat.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neuter |
Gender | - |
nom |
Case | - |
acc |
Case | - |
gen |
Case | - |
dat |
Case | - |
abl |
Case | - |
voc |
Case | - |
plural |
Number | - |
singular |
Number | - |
missing |
Coordinator | - |
mkN |
(verbum : Str) -> N |
- |
mkN |
(verbum, verbi : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
pluralN |
N -> N |
- |
singularN |
N -> N |
- |
constN |
Str -> Gender-> N |
- |
mkA |
(verbum : Str) -> A |
Nominative masculine |
mkA |
(verbum, verbi : Str) -> A |
Nominative and Genitive masculine |
mkA |
(bonus,bona,bonum : Str) -> A |
Nominative masculine, feminine and neuter |
mkA |
(verbum : Str) -> (comparable : Bool) -> A |
- |
constA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkV |
(tacere : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(iacere,iacio,ieci,iactus : Str) -> V |
- |
mkV |
(iacere,iacio,ieci : Str) -> V |
- |
V0 |
Type | - |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
- |
mkV0 |
Str -> V0 |
- |
mkV2 |
(amare : Str) -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
(facere : V) -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
constV |
Str -> Verb |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdv |
(pos,comp,super : Str) -> Adv |
- |
mkAdv |
(pos,comp : Str) -> Adv |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Coordinator -> Conjunction |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Coordinator -> Conjunction |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Coordinator -> Conjunction |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Preposition |
- |
mkPN |
N -> Number -> PN |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Bool -> V2V |
- |
mkVV |
V -> Bool -> CatLat.VV |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
AS |
Type | - |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
A2V |
Type | - |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
- |
AV |
Type | - |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
- |
Paradigms for Latvian
source ../../src/latvian/ParadigmsLav.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
nominative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
locative |
Case | - |
second_conjugation |
Conjugation | - |
third_conjugation |
Conjugation | - |
active_voice |
Voice | - |
passive_voice |
Voice | - |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Bool -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Declension -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Gender -> Bool -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Declension -> Bool -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Gender -> Declension -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Gender -> Declension -> Bool -> N |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> PN |
- |
mkN |
(lemma : Str) -> Number -> PN |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Bool -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkA |
(lemma : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(lemma : Str) -> AType -> A |
- |
mkA |
(v : V) -> Voice -> A |
- |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
- |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
- |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Case -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Conjugation -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Conjugation -> Case -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Str -> Str -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Case -> V |
- |
--mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
--mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
mkVS |
V -> Subj -> VS |
- |
mkVS |
V -> Subj -> Case -> VS |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> Case -> VQ |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkVV |
V -> Case -> VV |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Subj -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Case -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Case -> Prep |
- |
nom_Prep |
Prep | - |
gen_Prep |
Prep | - |
dat_Prep |
Prep | - |
acc_Prep |
Prep | - |
loc_Prep |
Prep | - |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkCAdv |
Str -> Str -> Degree -> CAdv |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkNumReg |
Str -> Str -> Number -> { s : DForm => CardOrd => Gender => Case => Str } |
- |
mkNumSpec |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> { s : DForm => CardOrd => Gender => Case => Str } |
- |
simts |
CardOrd => Gender => Number => Case => Str |
- |
tuukstotis |
CardOrd => Gender => Number => Case => Str |
- |
Paradigms for Maltese
source ../../src/maltese/ParadigmsMlt.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
form1 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan I: daħal |
form2 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan II: daħħal |
form3 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan III: wieġeb |
form4 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan IV: wera |
form5 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan V: ddaħħal |
form6 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan VI: twieġeb |
form7 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan VII: ndaħal |
form8 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan VIII: ftakar |
form9 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan IX: sfar |
form10 |
VDerivedForm | Binyan X: stieden |
strong |
VClass | Strong tri. verb: kiteb (k-t-b) |
liquidMedial |
VClass | Strong liquid-medial tri. verb: ħareġ (ħ-r-ġ) |
geminated |
VClass | Strong geminated tri. verb: ħabb (ħ-b-b) |
assimilative |
VClass | Weak-initial tri. verb: wieġeb (w-ġ-b) |
hollow |
VClass | Weak-medial tri. verb: ried (r-j-d) |
lacking |
VClass | Weak-final tri. verb: mexa (m-x-j) |
defective |
VClass | GĦ-final tri. verb: qata' (q-t-għ) |
quad |
VClass | Strong quad. verb: ħarbat (ħ-r-b-t) |
quadWeak |
VClass | Weak-final quad. verb: kanta (k-n-t-j) |
irregular |
VClass | Irregular verb: af ('-'-f) |
loan |
VClass | Loan verb: ipparkja (no root) |
mkN |
Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 1: Take the singular and infer plural |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
Noun paradigm 1: Explicit gender |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 1: Take the singular and explicit plural |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> Gender -> N |
Noun paradigm 1: Explicit gender |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 1x: Take singular and both plurals |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Gender -> N |
Noun paradigm 1x: Explicit gender |
mkNColl |
Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 2c: Collective form only |
mkNColl |
Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 2b: Collective and plural |
mkNColl |
Str -> Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 2: Singular, collective and plural |
mkNColl |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 2x: Singular, collective and both plurals |
mkNNoPlural |
Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 3: No plural |
mkNNoPlural |
Str -> Gender -> N |
Noun paradigm 3: Explicit gender |
mkNDual |
Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 4: Infer dual, plural and gender from singular |
mkNDual |
Str -> Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 4: Singular, dual, plural |
mkNDual |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Gender -> N |
Noun paradigm 4: Explicit gender |
mkNDual |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> N |
Noun paradigm 4x: Singular, dual, both plurals |
mkNDual |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Gender -> N |
Noun paradigm 4x: Explicit gender |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> Number -> ProperNoun |
Proper noun |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Str -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
use "ta'" |
mkN3 |
Noun -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
possN |
N -> N |
Mark a noun as taking possessive enclitic pronouns: missieri, missierek... |
mkRoot |
Root | Null root |
mkRoot |
Str -> Root |
From hyphenated string: "k-t-b" |
mkRoot |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Root |
Tri-consonantal root |
mkRoot |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Root |
Quadri-consonantal root |
mkVowels |
Vowels | Null vowel sequence |
mkVowels |
Str -> Vowels |
Only single vowel |
mkVowels |
Str -> Str -> Vowels |
Two-vowel sequence |
mkV |
Str -> V |
With no root, automatically treat as loan verb |
mkV |
Str -> Root -> V |
Take an explicit root, implying it is a root & pattern verb |
mkV |
Str -> Str -> Root -> V |
Takes an Imperative of the word for when it behaves less predictably |
mkV |
VClass -> VDerivedForm -> Root -> Vowels -> (_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_,_ : Str) -> V |
All forms: mkV (Strong Regular) (FormI) (mkRoot "k-t-b") (mkVowels "i" "e") "ktibt" "ktibt" "kiteb" "kitbet" "ktibna" "ktibtu" "kitbu" "nikteb" "tikteb" "jikteb" "tikteb" "niktbu" "tiktbu" "jiktbu" "ikteb" "iktbu" |
mkV_II |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form II verb: mkV_II "waqqaf" (mkRoot "w-q-f") |
mkV_II |
Str -> Str -> Root -> V |
Form II verb with explicit imperative form: mkV_II "waqqaf" "waqqaf" (mkRoot "w-q-f") |
mkV_III |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form III verb: mkV_III "qiegħed" (mkRoot "q-għ-d") |
mkV_V |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form V verb: mkV_V "twaqqaf" (mkRoot "w-q-f") |
mkV_VI |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form VI verb: mkV_VI "tqiegħed" (mkRoot "q-għ-d") |
mkV_VII |
Str -> Str -> Root -> V |
Form VII verb: mkV_VII "xeħet" "nxteħet" (mkRoot "x-ħ-t") |
mkV_VIII |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form VIII verb: mkV_VIII "xteħet" (mkRoot "x-ħ-t") |
mkV_IX |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form IX verb: mkV_IX "sfar" (mkRoot "s-f-r") |
mkV_X |
Str -> Root -> V |
Form X verb: mkV_X "stagħġeb" (mkRoot "għ-ġ-b") |
presPartV |
Str -> V -> V |
Add the present participle to a verb: ħiereġ |
presPartV |
Str -> Str -> Str -> V -> V |
Add the present participle to a verb: ħiereġ, ħierġa, ħierġin |
pastPartV |
Str -> V -> V |
Add the past participle to a verb: miktub |
pastPartV |
Str -> Str -> Str -> V -> V |
Add the past participle to a verb: miktub, miktuba, miktubin |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
sentence-compl |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
ditransitive: give,_,_ |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
two prepositions: speak, with, about |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
one preposition: give,_,to |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
want (noPrep NP) (to VP) |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
Conjunction: wieħed tnejn u tlieta |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
Conjunction: wieħed , tnejn u tlieta |
mkA |
Str -> A |
Regular adjective with predictable feminine and plural forms: bravu |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A |
Infer feminine from masculine; no comparative form: sabiħ, sbieħ |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> Str -> A |
Explicit feminine form; no comparative form: sabiħ, sabiħa, sbieħ |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> A |
All forms: sabiħ, sabiħa, sbieħ, isbaħ |
sameA |
Str -> A |
Adjective with same forms for masculine, feminine and plural: blu |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
post-verbal adverb: illum |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
preverbal adverb: dejjem |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
adverb modifying adjective: pjuttost |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
adverb modifying numeral: madwar |
Paradigms for Mongolian
source ../../src/mongolian/ParadigmsMon.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
mkN |
(_,_ : Str) -> Noun |
- |
mk2N |
(adj : Str) -> Noun -> Noun |
- |
mkLN |
(_,_ : Str) -> Noun |
- |
regN |
Str -> Noun |
- |
loanN |
Str -> Noun |
- |
modDecl |
(Dcl -> Dcl) -> Str -> Noun |
- |
modDeclL |
(Dcl -> Dcl) -> Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01a |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01b |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01c |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01d |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01e |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01f |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01g |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN01h |
Str -> Noun |
- |
mkLN01c |
Str -> Noun |
- |
modDecl2 |
(Dcl -> Dcl) -> Str -> Str -> Noun |
- |
modDecl2L |
(Dcl -> Dcl) -> Str -> Str -> Noun |
- |
reg2N |
(nomSg,nomPl : Str) -> Noun |
- |
loan2N |
(nomSg,nomPl : Str) -> Noun |
- |
mkN02a |
(nomSg,nomPl : Str) -> Noun |
- |
mkN02b |
(nomSg,nomPl : Str) -> Noun |
- |
mkN02c |
Str -> Str -> Noun |
- |
mkN02d |
(nomSg,nomPl : Str) -> Noun |
- |
mkN02e |
(nomSg,nomPl : Str) -> Noun |
- |
mkNP |
Str -> Def -> NP |
- |
regV |
Str -> Verb |
- |
verbToAux |
Verb -> Aux |
- |
auxToVerb |
Aux -> Verb |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Verb |
- |
auxBe |
Aux | - |
Paradigms for Nepali
source ../../src/nepali/ParadigmsNep.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
human |
NType | - |
profession |
NType | - |
living |
NType | - |
regN |
Str -> N |
- |
regN |
Str -> NPerson -> N |
- |
regN |
Str -> NType -> N |
- |
regN |
Str -> NType -> NPerson -> N |
- |
mkNF |
Str -> N |
- |
mkNF |
Str -> NPerson -> N |
- |
mkNF |
Str -> NType -> N |
- |
mkNF |
Str -> NType -> NPerson -> N |
- |
mkNUC |
Str -> N |
- |
mkNUC |
Str -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkNUC |
Str -> Gender -> NType -> N |
- |
mkNUC |
Str -> Gender -> NType -> NPerson -> N |
- |
--mkNUC |
Str -> NType -> Gender -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> NType -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> NType -> NPerson -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> N2; |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> Str-> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> Str-> NType -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> Str-> N3 |
- |
mkCmpdNoun |
Str -> N -> N |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> NPerson -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> NType -> NPerson -> PN |
- |
mkPron |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Gender -> NPerson -> Pron |
- |
mkPron |
(x1,_,_,_,_,_,x7 : Str) -> Number -> Gender -> NPerson -> Pron |
- |
demoPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Quant |
- |
mkDet |
(s1,s2:Str) -> Number -> Det |
- |
mkDet |
(s1,s2,s3,s4:Str) -> Number -> Det |
- |
mkIDetn |
(s1,s2:Str) -> Number -> IDet |
- |
mkIP |
(x1,x2,x3,x4:Str) -> Number -> IP |
- |
mkA |
Str-> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> V3 |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Str -> Bool -> V2V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V -> V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V2 -> V |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
e.g. today |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
e.g. always |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
e.g. quite |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
e.g. approximately |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
noPrep |
Prep | - |
--mkQuant |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkQuant |
(s1,s2,s3,s4:Str) -> Quant |
- |
mkQuant |
(s1,s2:Str) -> Quant |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and (plural agreement) |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
both ... and (plural) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either ... or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
Paradigms for Norwegian (nynorsk)
source ../../src/nynorsk/ParadigmsNno.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | the "ein" gender |
feminine |
Gender | the "ei" gender |
neutrum |
Gender | the "eit" gender |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
e.g. "etter" |
noPrep |
Prep | empty string |
mkN |
Str -> N |
predictable noun, feminine for "-e" otherwise masculine |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
force gender |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenger,drengene : Str) -> N |
worst case |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. datter + til |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g forbindelse + fra + til |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
masculine |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
force gender |
mkA |
(fin : Str) -> A |
predictable adjective |
mkA |
(fin,fint : Str) -> A |
deviant neuter |
mkA |
(galen,galet,galne : Str) -> A |
also plural deviant |
mkA |
(stor,stort,store,storre,storst : Str) -> A |
worst case |
mkA |
A -> A |
comparison with mer/mest, e.g. "norsk" |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. gift + med |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
e.g. her |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
e.g. altid |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
e.g. mye |
mkV |
(snakke : Str) -> V |
regular verb (first conjugation) |
mkV |
(leve,levde : Str) -> V |
other past tense |
mkV |
(drikke, drakk, drukket : Str) -> V |
theme of irregular verb |
mkV |
(spise,spiser,spises,spiste,spist,spis : Str) -> V |
worst case |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
verb with particle, e.g. lukke + opp |
vaereV |
V -> V |
force "være" as auxiliary (default "have") |
depV |
V -> V |
deponent, e.g "trives" |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive, e.g. "forestille seg" |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
regular, direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
preposition for complement |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
snakke, med, om |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
gi,_,til |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
gi,_,_ |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for Norwegian (bokmål)
source ../../src/norwegian/ParadigmsNor.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | the "en" gender |
feminine |
Gender | the "ei" gender |
neutrum |
Gender | the "et" gender |
utrum |
Gender | the "en" gender, same as masculine |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
e.g. "etter" |
noPrep |
Prep | empty string |
mkN |
Str -> N |
predictable noun, feminine for "-e" otherwise masculine |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
force gender |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenger,drengene : Str) -> N |
worst case, gender guessed |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenger,drengene : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. datter + til |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g forbindelse + fra + til |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
masculine |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
force gender |
mkA |
(fin : Str) -> A |
predictable adjective |
mkA |
(fin,fint : Str) -> A |
deviant neuter |
mkA |
(galen,galet,galne : Str) -> A |
also plural deviant |
mkA |
(stor,stort,store,storre,storst : Str) -> A |
worst case |
mkA |
A -> A |
comparison with mer/mest, e.g. "norsk" |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. gift + med |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
e.g. her |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
e.g. altid |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
e.g. mye |
mkV |
(snakke : Str) -> V |
regular verb (first conjugation) |
mkV |
(leve,levde : Str) -> V |
other past tense |
mkV |
(drikke, drakk, drukket : Str) -> V |
theme of irregular verb |
mkV |
(spise,spiser,spises,spiste,spist,spis : Str) -> V |
worst case |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
verb with particle, e.g. lukke + opp |
vaereV |
V -> V |
force "være" as auxiliary (default "have") |
depV |
V -> V |
deponent, e.g "trives" |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive, e.g. "forestille seg" |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
regular, direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
preposition for complement |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
snakke, med, om |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
gi,_,til |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
gi,_,_ |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for Persian
source ../../src/persian/ParadigmsPes.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Animacy |
Type | Argument to mkN |
human |
Animacy | e.g. /mkN "خواهر" human/ to get the plural خواهران. |
nonhuman |
Animacy | default animacy for mkN, not needed unless you want to make the animacy explicit or force a plural with ها. |
Number |
Type | Argument to mkDet and mkConj |
singular |
Number | e.g. mkConj "یا" singular |
plural |
Number | e.g. mkConj "و" plural |
VVForm |
Type | Argument to mkVV |
subjunctive |
VVForm | The verbal complement of VV is in subjunctive |
indicative |
VVForm | The verbal complement of VV is in indicative |
Mod |
Type | Argument to mkDet and mkPrep |
ezafe |
Mod | e.g. mkPrep "برای" ezafe |
mkN |
(sg : Str) -> N |
Takes singular form, returns a nonhuman noun with ها as the plural form. |
mkN |
(sg : Str) -> Animacy -> N |
Takes singular form and animacy. Nonhuman plural ها. Human plural ان or an allomorph of it (یان or گان) depending on the singular form. |
mkN |
(sg,pl : Str) -> Animacy -> N |
Worst-case constructor: takes singular, plural and animacy. Use for loanwords with Arabic plural, human plurals with ها and nonhuman plurals with ان or its allomorphs. |
mkN |
(possStem : Str) -> N -> N |
Noun with an unexpected possessive stem, e.g. مه where ه is a consonant, not vowel. |
mkN2 |
(key : N) -> (to : Str) -> N2 |
Takes a noun and a complementiser as a string, returns a N2. |
mkN2 |
(key : N) -> (to : Prep) -> N2 |
Takes a noun and a complementiser as a Prep, returns a N2. |
mkN3 |
(distance : N) -> (from,to : Str) -> N3 |
Takes a noun and two complementisers as strings, returns a N3. |
mkN3 |
(distance : N) -> (from,to : Prep) -> N3 |
Takes a noun and two complementisers as Preps, returns a N3. |
cmpdN |
Str -> N -> N |
Compound noun with an invariable modifier /before/ the head. NB. no ezāfe. |
cmpdN |
N -> Str -> N |
Compound noun with an invariable modifier /after/ the head. NB. no ezāfe. |
cmpdN |
N -> N -> N |
Compound noun with ezafe (Nی N) |
mkPN |
Str -> Animacy -> PN |
Proper noun with given animacy |
mkDet |
Str -> Number -> Det |
Takes a string, number (sg/pl) and returns a det which is not a numeral |
mkDet |
Str -> Number -> (isNum : Bool) -> Det |
As above + a Boolean for whether the det is a numeral |
mkDet |
Str -> Number -> (isNum, isNeg : Bool) -> Det |
As above + a Boolean for whether the det is negative |
mkDet |
Str -> Number -> (isNum, isNeg : Bool) -> Mod -> Det |
As above + Mod for which form the determiner expects its argument to be (default bare) |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
Regular adjective, same form for adjective and adverb. |
mkA |
(adj,adv : Str) -> A |
Different forms for adjective and adverb. |
prefixA |
A -> A |
Adjective that comes before the noun |
mkA2 |
(married,to : Str) -> A2 |
Takes string and complementiser, returns A2. |
mkV |
(inf : Str) -> V |
Takes infinitive. Use for predictable verbs: if it ends in vowel+دن, the present stem removes the vowel as well. If it ends in consonant+تن or consonant+دن, present stem only removes تن/دن. |
mkV |
(inf,pres : Str) -> V |
Takes infinitive and present root. Use for unpredictable verbs, e.g. دانستن with present stem دان, or irregular, e.g. کردن with present stem کن. |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
Invariable prefix to a verb, e.g. mkV "دوست" haveVerb |
invarV |
Str -> V |
no inflection at all |
defV |
(inf,pres,past : Str) -> V |
no personal forms, but past/present difference, like بایستن ('must'), |
haveVerb |
V | The verb "have", to be used for light verb constructions: e.g. compoundV "دوست" haveVerb. NB. this has different imperative and VV forms from StructuralPes.have_V2. |
beVerb |
V | The verb "be", to be used for light verb constructions: e.g. compoundV "عاشق" beVerb. |
doVerb |
V | The verb "do", to be used for light verb constructions. In passive, is replaced by شدن. |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
Predictable V2 out of string. No preposition, را for direct object. |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
V2 out of V. No preposition, را for direct object. |
mkV2 |
(listen : V) -> (to : Prep) -> V2 |
V2 out of V. Use given preposition, no را for direct object. |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
Predictable V3, را for direct object, no prepositions. |
mkV3 |
V -> (dir,indir : Str) -> V3 |
Takes a verb and two prepositions or را as strings (can be empty). |
mkV3 |
V -> (dir,indir : Prep) -> V3 |
Takes a verb and two prepositions |
mkVQ |
Str -> VQ |
predictable verb with question complement |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
VQ out of a verb |
mkVA |
Str -> VA |
predictable verb with adjective complement |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
VA out of a verb |
mkVA |
V -> Prep -> VA |
VA out of a verb and preposition |
mkVS |
Str -> VS |
predictable verb with sentence complement in subjunctive. |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
VS out of a verb, sentence complement in subjunctive. |
mkVS |
VVForm -> V -> VS |
sentence complement given as argument |
mkVV |
Str -> VV |
Predictable VV, subjunctive complement, is auxiliary. |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
takes its VP complement in subjunctive. Is auxiliary. |
mkVV |
VVForm -> V -> VV |
takes its VP complement in the given VVForm |
mkVV |
(isAux : Bool) -> VVForm -> V -> VV |
takes its VP complement in the given VVForm. Whether it's auxiliary (T/F) given as the first argument. |
defVV |
VV -> VV |
- |
mkV2S |
Str -> V2S |
predictable morphology, direct object with را, sentence complement in subjunctive. |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
direct object with را, sentence complement in subjunctive. |
mkV2S |
Prep -> VVForm -> V -> V2S |
direct object and mood for sentence complement as arguments. |
mkV2S |
V2 -> V2S |
direct object given by V2, sentence complement in subjunctive. |
mkV2S |
VS -> V2S |
direct object with را, sentence complement given by VS. |
mkV2V |
V -> (cN : Str) -> (isAux : Bool) -> V2V |
Verb, complementiser for the noun, whether it's auxiliary. |
mV2V |
VV -> (cN : Str) -> V2V |
V2V out of VV + complementiser for the noun |
mV2V |
VV -> V2V |
V2V out of VV, را for direct object |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
Takes a string, returns an adverb. |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
Takes a string, returns a preposition. |
mkPrep |
Str -> Mod -> Prep |
Takes a string and Mod (so far only option is ezafe), returns a preposition. |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and (plural agreement) |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
both ... and (plural) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either ... or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkSubj |
Str -> Subj |
Takes its verbal complement in indicative. |
mkSubj |
VVForm -> Str -> Subj |
Specify whether it takes complement in subjunctive or indicative. |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
Paradigms for Punjabi
source ../../src/punjabi/ParadigmsPnb.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number; |
- |
plural |
Number; |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> N2; |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> Str-> N3 |
- |
mkCmpdNoun |
Str -> N -> N |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
- |
personalPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Gender -> PPerson -> Pron |
- |
demoPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Quant |
- |
mkDet |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Det |
- |
mkIP |
(x1,x2,x3,x4:Str) -> Number -> Gender -> IP |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkA |
Str-> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> V3; |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Str -> Bool -> V2V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V -> V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V2 -> V |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkQuant1 |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkIQuant |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> IQuant |
- |
mkQuant1 |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and (plural agreement) |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
both ... and (plural) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either ... or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
Paradigms for Polish
source ../../src/polish/ParadigmsPol.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
ComplCase |
Type | - |
genPrep |
ComplCase | - |
genNoPrep |
ComplCase | - |
datPrep |
ComplCase | - |
datNoPrep |
ComplCase | - |
mkN |
Str -> N |
One argument: singular nominative |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N ;-- Two arguments: singular nom, gender |
- |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> N |
Two arguments: sgnom, sggen |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> ComplCase -> A2 |
- |
Paradigms for Portuguese
source ../../src/portuguese/ParadigmsPor.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
accusative |
Prep | direct object |
genitive |
Prep | preposition "de" and its contractions |
dative |
Prep | preposition "a" and its contractions |
CopulaType |
Type | - |
serCopula |
CopulaType | - |
estarCopula |
CopulaType | - |
ficarCopula |
CopulaType | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
other preposition |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
compound prepositions, e.g. "antes de", made as mkPrep "antes" genitive |
mkN |
(revolução : Str) -> N |
predictable nouns |
mkN |
(alemão, alemães : Str) -> N |
force noun plural, guess gender |
mkN |
(mapa : Str) -> Gender -> N |
force gender, guess plural |
mkN |
(mão, mãos : Str) -> Gender -> N |
the worst case demands two forms (singular + plural) and the gender. |
mkN |
(número : N) -> (de_telefone : Str) -> N |
compound noun with non-inflecting second art, e.g. "número" + "de telefone" |
mkN |
(forma, finita : N) -> N |
compound with inflecting second part, e.g. "forma" + "finita" |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition, e.g. "comida para (viagem)" |
deN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition "de", e.g. "filho de (fulano)" |
aN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition "a", e.g. "molho a francesa" |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
relational noun with two prepositions for two complements, e.g. "a relação de (fulana) com (cicrana)" |
mkPN |
(Anna : Str) -> PN |
regular proper noun: feminine for "-a", else masculine |
mkPN |
(Pilar : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
force gender of proper noun |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
build proper noun from noun, taking gender and singular form |
invarA |
Str -> A |
invariable adjective, e.g. "simples" |
mkNonInflectA |
A -> Str -> A |
- |
mkA |
(bobo : Str) -> A |
predictable adjective |
mkA |
(espanhol,espanhola : Str) -> A |
some adjectives need the feminine form separately |
mkA |
(burrão,burrona,burrões,burronas : Str) -> A |
provide masculine and feminine singular and plural forms (very rarely does one need to specify the adverbial form) |
mkA |
(gabarolas,gabarolas,gabarolas,gabarolas,gabarolamente : Str) -> A |
one-place adjectives compared with "mais" need five forms in the worst case (masc and fem singular, masc and fem plural, adverbial). |
mkA |
(bom : A) -> (melhor : A) -> A |
two separate adjectives are given: the positive ("bom"), and the comparative ("melhor"). Comparison with "mais" is the default. |
mkA |
(blanco : A) -> (hueso : Str) -> A |
noninflecting component after the adjective |
mkA |
A -> CopulaType -> A |
force copula type, e.g. "João está doente" instead of "João é doente". Choose among serCopula, estarCopula, and ficarCopula. |
prefixA |
A -> A |
adjective before noun (default after noun) |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
two-place adjectives, e.g. "casado" + "com" |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
after the verb adverb |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
before the verb adverb, e.g. "nunca" |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
adverb modifying adjectives, e.g. "muito" |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
adverb modifying numeral, e.g. "pelo menos" |
VType |
Type | verb is reflexive / verb uses auxiliar X |
auxTer |
VType | "ter" as auxiliary verb |
auxHaver |
VType | "haver" as auxiliary verb |
auxRefl |
VType | verb is reflexive |
mkV |
(pagar : Str) -> V |
predictable verb, e.g., "comer", "chamar-se" |
mkV |
(abrir,aberto : Str) -> V |
deviant past participle, e.g. abrir - aberto |
mkV |
Verbum -> V |
import verb constructed with BeschPor |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
particle verb |
mkV |
V -> VType -> V |
choose auxiliary verb or make verb reflexive |
reflV |
V -> V |
force reflexive verb, e.g. reflV "chamar" |
special_ppV |
V -> Str -> V |
force past participle, e.g. abrir - aberto |
mkV2 |
(amar : Str) -> V2 |
predictable verb with direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
verb with direct object (no preposition) |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
verb with other object |
v2V |
V2 -> V |
coerce V2 to V |
mkV3 |
(dar : Str) -> V3 |
dar (+ accusative + dative), e.g. "ele dá um cachorro a Paris" |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
dar (+ accusative + dative) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
force one preposition, e.g. "ele vende a João um cachorro" |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
force prepositions, e.g. "ela fala de Paris a João" |
V0 |
Type | zero-place verbs, e.g. "chover" |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
"chover" |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
complement sentence in the indicative mood, e.g. "eu sei que meu cachorro viverá" |
subjVS |
V -> VS |
complement sentence in the subjunctive mood, e.g. "eu temo que meu cachorro morra" |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
plain infinitive: "quero falar" |
deVV |
V -> VV |
"terminar de falar" |
aVV |
V -> VV |
"aprender a falar" |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
"ela se tornou direta" |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
"nós nos perguntamos se você ama alguém" |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
"pergunte a João se ele bebe água" |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
"ele respondeu a João que ela vivia" |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
force preposition |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
verb with verb complement in the accusative and NP complement in the dative |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
"ele rogou a Paris para viver" |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
verb with NP and AP complement (in the dative) |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
ele pintou a casa de branco |
Paradigms for Romanian
source ../../src/romanian/ParadigmsRon.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
NGender |
Type | - |
masculine |
NGender | - |
feminine |
NGender | - |
neuter |
NGender | - |
Gender |
Type | - |
Masculine |
Gender | - |
Feminine |
Gender | - |
Anim |
Type | - |
animate |
Anim | - |
inanimate |
Anim; |
- |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
Preposition |
Type | - |
NCase |
Type | - |
Acc |
NCase | - |
Dat |
NCase | - |
Gen |
NCase | - |
Nom |
NCase | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> NCase-> Bool -> Prep |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> NCase -> Prep; |
- |
noPrep |
NCase -> Prep |
- |
mkN |
Str -> N |
Singular, infers gender and Plural |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> NGender -> N |
worst case: Singular + Plural + gender |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> N |
very irregular nouns - feminine |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> N |
Singular + Plural, infers gender |
mkN |
Str -> NGender -> N |
Singular + gender, infers Plural |
mkNR |
Str -> N; |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Str -> Gender -> Number -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> Number -> PN |
- |
mkInAn |
PN -> PN |
- |
mkPropNoun |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
regular adjectives |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> A --worst case |
all 4 forms are needed + form for adverb |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> A |
4 forms are needed |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
Paradigms for Russian
source ../../src/russian/ParadigmsRus.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neuter |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
only_singular |
MaybeNumber | - |
only_plural |
MaybeNumber | - |
short |
ShortFormPreference | - |
full |
ShortFormPreference | - |
animate |
Animacy | - |
inanimate |
Animacy | - |
nominative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
instrumental |
Case | - |
prepositional |
Case | - |
locative |
Case | or Pre-2, some nouns have this different from prepositional case |
partitive |
Case | or Gen-2. Some nouns like "tee", have this in addition to genitive, usually spoken language |
vocative |
Case | can be used in spoken language |
positive |
Degree | - |
comparative |
Degree | - |
superlative |
Degree | - |
perfective |
Aspect | - |
imperfective |
Aspect | - |
transitive |
Transitivity | - |
intransitive |
Transitivity | - |
reflexive |
Reflexivity | - |
non_reflexive |
Reflexivity | - |
active |
Voice | - |
passive |
Voice | - |
mkN |
Str -> N |
can guess declension and gender of some nouns given nominative |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> Animacy -> N |
can guess declension of more nouns |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> Animacy -> (idx : Str) -> N |
Fourth parameter is a declension type index (based on Zaliznyak's dictionary), for example, "1*a(1)" |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> Animacy -> (idx : Str) -> MaybeNumber -> N |
Same, but number restrictions can be added |
mkN |
A -> Gender -> Animacy -> N |
for nouns, which decline as adjective |
mkN |
A -> Gender -> Animacy -> MaybeNumber -> N |
same, with possibility to limit number (usually to only_singular) |
mkN |
N -> (link : Str) -> N -> N |
compound noun. Link can end on "-", in which case parts are glued together. First one characterizes the whole. |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
- |
mkN2 |
Str -> Gender -> Animacy -> (idx : Str) -> Prep -> N2 |
convenience for making N2. Fourth parameter is a declension type index (based on Zaliznyak's dictionary), for example, "1*f''(1)" |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
- |
mkN3 |
Str -> Gender -> Animacy -> (idx : Str) -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
convenience for making N2. Fourth parameter is a declension type index (based on Zaliznyak's dictionary), for example, "4*b" |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
N -> Str -> N -> PN |
see compound noun |
mkA |
Str -> A |
can guess declension of many adjectives given nominative masculine |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A |
same, but comparative given as a second argument |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> (idx : Str) -> A |
nom masc, comparative and third parameter is Zaliznyak's dictionary index, for example, "1a" |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> (idx : Str) -> ShortFormPreference -> A |
same, but with short form preference given |
mkA |
Str -> ZAIndex -> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> ZAIndex -> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> ZAIndex -> ShortFormPreference -> A |
- |
mkA |
A -> Str -> A -> A |
Compound adjective like социально-экономический |
mkA |
V -> Voice -> Tense -> A |
make participles |
ShortenA |
A -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkOrd |
(nom : Str) -> Ord |
- |
mkV |
(inf : Str) -> (sg1 : Str) -> V |
guess some I conjugation verbs (not "ё") from infinitive and Sg P1, perfective, transitive |
mkV |
(inf : Str) -> (sg1 : Str) -> (sg3 : Str) -> V |
guess verb forms given Inf, Sg P1, Sg P3, perfective, transitive |
mkV |
Aspect -> (inf : Str) -> (sg1 : Str) -> (sg3 : Str) -> V |
same, but aspect as first parameter |
mkV |
Aspect -> Transitivity -> (inf : Str) -> V |
for irregular verbs |
mkV |
Aspect -> Transitivity -> (inf : Str) -> (sg1 : Str) -> (sg3 : Str) -> V |
aspect, transitivity, Inf, Sg P1, Sg P3 |
mkV |
Aspect -> Transitivity -> (inf : Str) -> (sg1 : Str) -> (sg3 : Str) -> (idx : Str) -> V |
aspect, transitivity, Inf, Sg P1, Sg P3 and index from Zaliznyak's dictionary, eg "14a" |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
most common case with Acc and no preposition |
mkV2 |
V -> Case -> V2 |
given case, but no preposition |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Case -> Case -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
dirV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
tvDirDir |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV; |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkIAdv |
Str -> IAdv |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
only middle conjunction |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
two-part conjunction |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
- |
Paradigms for Slovak
source ../../src/slovak/ParadigmsSlo.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mascAnimate |
Gender | - |
mascInanimate |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
neuter |
Gender | - |
nominative |
Case | - |
genitive |
Case | - |
dative |
Case | - |
accusative |
Case | - |
locative |
Case | - |
instrumental |
Case | - |
mkN |
(nom : Str) -> N |
- |
mkN |
(nom,gen : Str) -> Gender -> N |
- |
chlapN |
Str -> N |
- |
hrdinaN |
Str -> N |
- |
dubN |
Str -> N |
- |
strojN |
Str -> N |
- |
ponyN |
Str -> N |
- |
zenaN |
(snom, pgen : Str) -> N |
- |
ulicaN |
(snom, pgen : Str) -> N |
- |
dlanN |
(snom, pgen : Str) -> N |
- |
kostN |
(snom, pgen : Str) -> N |
- |
mestoN |
(snom, pgen : Str) -> N |
- |
srdceN |
(snom, pgen : Str) -> N |
- |
vysvedcenieN |
Str -> N |
- |
dievcaN |
Str -> N |
- |
dievceniecN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
- |
peknyA |
Str -> A |
- |
krasnyA |
Str -> A |
- |
cudziA |
Str -> A |
- |
rydziA |
Str -> A |
- |
otcovA |
Str -> A |
- |
paviA |
Str -> A |
- |
invarA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
- |
mkV2 |
VerbForms -> VerbForms ** {c : ComplementCase} |
- |
mkV2 |
VerbForms -> Case -> VerbForms ** {c : ComplementCase} |
- |
mkV2 |
VerbForms -> ComplementCase -> VerbForms ** {c : ComplementCase} |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
Paradigms for Sindhi
source ../../src/sindhi/ParadigmsSnd.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number; |
- |
plural |
Number; |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> N2; |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> Str-> N3 |
- |
mkCmpdNoun |
Str -> N -> N |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
- |
personalPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Gender -> PPerson -> Pron |
- |
demoPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Quant |
- |
mkDet |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Det |
- |
mkIP |
(x1,x2,x3,x4:Str) -> Number -> Gender -> IP |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkA |
Str-> A |
- |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> V3; |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Str -> Bool -> V2V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V -> V |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V2 -> V |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
mkQuant1 |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkIQuant |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> IQuant |
- |
mkQuant1 |
Pron -> Quant |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and (plural agreement) |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
both ... and (plural) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either ... or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
Paradigms for Spanish
source ../../src/spanish/ParadigmsSpa.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
accusative |
Prep | direct object |
genitive |
Prep | preposition "de" and its contractions |
dative |
Prep | preposition "a" and its contractions |
CopulaType |
Type | - |
serCopula |
CopulaType | - |
estarCopula |
CopulaType | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
other preposition |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep -> Prep |
compound prepositions, e.g. "antes de", made as mkPrep "antes" genitive |
mkN |
(luz : Str) -> N |
predictable; feminine for "-a"/"-z", otherwise masculine |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
force gender |
mkN |
(baston,bastones : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case |
mkN |
N -> Str -> N |
compound, e.g. "número" + "de teléfono" |
compN |
N -> Str -> N |
compound, e.g. "número" + "de teléfono" |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition |
deN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition "de" |
aN2 |
N -> N2 |
relational noun with preposition "a" |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
prepositions for two complements |
mkPN |
(Anna : Str) -> PN |
feminine for "-a" |
mkPN |
(Pilar : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
force gender |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
gender from noun |
mkA |
(util : Str) -> A |
predictable adjective |
mkA |
(español,española : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(solo,sola,solos,solas,solamente : Str) -> A |
almost worst-case, except for buen/bueno gran/grande |
mkA |
(gran,grande,gran,grande,grandes,grandes,solamente : Str) -> A |
worst-case |
mkA |
(bueno : A) -> (mejor : A) -> A |
special comparison (default with "mas") |
mkA |
(blanco : A) -> (hueso : Str) -> A |
noninflecting component after the adjective |
mkA |
A -> CopulaType -> A |
force copula type |
prefixA |
A -> A |
adjective before noun (default after noun) |
invarA |
Str -> A |
invariable adjective |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. "casado" + dative |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkV |
(pagar : Str) -> V |
regular in "-ar", "-er", ".ir" |
mkV |
(mostrar,muestro : Str) -> V |
regular with vowel alternation |
mkV |
Verbum -> V |
import verb constructed with BeschSpa |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
particle verb |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive verb |
special_ppV |
V -> Str -> V |
deviant past participle, e.g. abrir - abierto |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
regular, direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct object |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
other object |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
donner (+ accusative + dative) |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
placer (+ accusative) + dans |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
parler + dative + genitive |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
e.g. dar,(accusative),a |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
e.g. dar,(dative),(accusative) |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
subjVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
plain infinitive: "quiero hablar" |
deVV |
V -> VV |
"terminar de hablar" |
aVV |
V -> VV |
"aprender a hablar" |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
Paradigms for Swedish
source ../../src/swedish/ParadigmsSwe.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gender |
Type | - |
utrum |
Gender | the "en" gender |
neutrum |
Gender | the "ett" gender |
Number |
Type | - |
singular |
Number | - |
plural |
Number | - |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
e.g. "till" |
noPrep |
Prep | empty string |
mkN |
(apa : Str) -> N |
predictable nouns: apa-apor, rike-riken, or bil-bilar |
mkN |
(nyckel,nycklar : Str) -> N |
singular and plural suffice for most nouns |
mkN |
(museum,museet,museer,museerna : Str) -> N |
worst case for nouns |
mkN |
(museum,museet,museer,museerna : Str) -> Gender -> N |
even worse case for nouns |
mkN |
(regering, makt : N) -> N |
regeringsmakt, using the co form of regering |
mkN |
Str -> N -> N |
över + flöde |
changeCompoundN |
Str -> N -> N |
kyrko + kyrka_N |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
e.g. summan - av |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
e.g. syster - till |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
e.g. flyg - från - till |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
default gender utrum |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
set other gender |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
get inflection and gender from a noun |
mkPN |
(jesus,jesu : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
irregular genitive |
mkA |
(billig : Str) -> A |
- |
mkA |
(bred,brett : Str) -> A |
predictable adjective |
mkA |
(tung,tyngre,tyngst : Str) -> A |
irregular comparison |
mkA |
(god,gott,goda,battre,bast : Str) -> A |
very irregular |
mkA |
(liten,litet,lilla,sma,mindre,minst,minsta : Str) -> A |
worst case |
compoundA |
A -> A |
force comparison by mera - mest |
invarA |
Str -> A |
e.g. äkta |
irregAdv |
A -> Str -> A |
adverb irreg |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
e.g. delbar - med |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
postverbal, e.g. här |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
preverbal, e.g. alltid |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
modify adjective, e.g. tämligen |
mkV |
(stämmer : Str) -> V |
predictable verb: use present indicative |
mkV |
(slita, slet : Str) -> V |
i/e/i, u/ö/u, u/a/u |
mkV |
(dricka,drack,druckit : Str) -> V |
the theme of an irregular verb |
mkV |
(gå,går,gå,gick,gått,gången : Str) -> V |
worst case |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
particle verb, e.g. passa - på |
depV |
V -> V |
deponent verb, e.g. andas |
reflV |
V -> V |
reflexive verb, e.g. ångra sig |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
direct transitive |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
preposition for complement |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
direct ditransitive |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
preposition for last argument |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
prepositions for both complements |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> V2S |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
- |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
auxVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
- |
auxV2V |
V -> V2V |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> V2A |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
- |
mkInterj |
Str -> Interj |
- |
Paradigms for Thai
source ../../src/thai/ParadigmsTha.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
mkN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN |
Str -> Str -> N |
- |
personN |
Str -> N |
- |
fooddishN |
Str -> N |
- |
vehicleN |
Str -> N |
- |
houseN |
Str -> N |
- |
animalN |
Str -> N |
- |
placeN |
Str -> N |
- |
verbalN |
Str -> N |
- |
mkN2 |
N -> Str -> N2 |
- |
mkN3 |
N -> Str -> Str -> N3 |
- |
mkA |
Str -> A |
- |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkV |
Str -> V |
- |
mkV |
Str -> Str -> V |
- |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> V3 |
- |
mkVV |
Str -> VV |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
- |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
- |
mkV2Q |
V -> Str -> V2Q |
- |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Str -> V2V |
- |
mkV2S |
V -> Str -> V2S |
- |
mkV2A |
V -> Str -> Str -> V2A |
- |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
- |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
- |
Paradigms for Urdu
source ../../src/urdu/ParadigmsUrd.gf
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
masculine |
Gender | - |
feminine |
Gender | - |
singular |
Number; |
- |
plural |
Number; |
- |
mkN |
Str -> N |
Regular nouns like lRka, gender is judged from noun ending |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
nouns whose gender is irregular like Admy |
mkN |
(x1,_,_,_,_,x6 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
worst case |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> N2; |
e.g maN ky |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Str -> Str-> N3 |
e.g faSlh - sE - ka |
mkCmpdNoun |
Str -> N -> N |
e.g t-alb elm |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
- |
personalPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Gender -> UPerson -> Pron |
- |
demoPN |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Quant |
- |
mkDet |
Str -> Str -> Str -> Str -> Number -> Det |
- |
mkIP |
(x1,x2,x3:Str) -> Number -> Gender -> IP |
- |
mkAdN |
Str -> AdN |
- |
mkA |
Str-> A |
e.g ach'a |
mkA |
Str -> Str -> A2 |
e.g sE Xady krna |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> A2 |
- |
mkCompoundA |
Str -> Str -> A |
e.g dra hwa |
mkV |
Str -> V |
regular verbs like swna |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
e.g pyna |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
e.g pyna |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> V2 |
e.g bnd krna |
dirV2 |
V -> V2 |
- |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> V3; |
e.g bycna |
mkV2V |
V -> Str -> Str -> Bool -> V2V |
e.g eltja krna - sE - kw |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
- |
compoundV |
Str -> V -> V |
e.g barX hwna |
compoundV |
Str -> V2 -> V |
e.g bnd krna |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
e.g yhaN |
mkAdv |
Str -> Str -> Adv |
- |
mkPrep |
Str -> Str -> Prep |
e.g ka - ky |
mkIQuant |
Str -> IQuant |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
and (plural agreement) |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
both ... and (plural) |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
either ... or (agrement number given as argument) |
mkConj |
Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Conj |
- |
mkConj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mk2Conj |
Str -> Str -> Number -> Conj |
- |
mkVS |
V -> VS; |
e.g drna |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
- |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
- |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
e.g janna |
Additional Libraries
The Prelude module
The Prelude defines commonly used utility functions, in particular for strings and booleans.
| Oper | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
SS |
Type |
the type {s : Str} |
ss |
Str -> SS |
record from string |
nonExist |
Str |
missing form |
optStr |
Str -> Str |
optional string |
bothWays |
(x,y : Str) -> Str |
either x ++ y or y ++ x |
Bool |
PType |
values True and False |
andB |
(_,_ : Bool) -> Bool |
conjunction |
orB |
(_,_ : Bool) -> Bool |
disjunction |
notB |
Bool -> Bool |
negation |
if_then_else |
(A:Type)->Bool->A->A->A |
conditional |
init |
Str -> Str |
drop last character |
last |
Str -> Str |
return last character |
glue |
Str -> Str -> Str |
glue tokens together |
The Predefined module
These functions are hard-coded in GF. They are available without explicit opening, by the used of qualified names, e.g. Predef.tk.
| Oper | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
PBool |
PType |
PTrue | PFalse |
Error |
Type |
the empty type |
Integer |
Type |
the type of integers |
Ints |
Integer -> Type |
integers from 0 to n |
error |
Str -> Error |
forms error message |
length |
Str -> Int |
length of string |
drop |
Integer -> Str -> Str |
drop prefix of length |
take |
Integer -> Str -> Str |
take prefix of length |
tk |
Integer -> Str -> Str |
drop suffix of length |
dp |
Integer -> Str -> Str |
take suffix of length |
eqInt |
Integer -> Integer -> PBool |
test if equal integers |
lessInt |
Integer -> Integer -> PBool |
test order of integers |
plus |
Integer -> Integer -> Integer |
add integers |
eqStr |
Str -> Str -> PBool |
test if equal strings |
occur |
Str -> Str -> PBool |
test if occurs as substring |
occurs |
Str -> Str -> PBool |
test if any char occurs |
show |
(P : Type) -> P -> Str |
convert param to string |
toStr |
(L : Type) -> L -> Str |
find the "first" string |
The Formal module
This module is used for defining formal languages, in particular ones that use precedence levels and parentheses for grouping subexpressions.
| Oper | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Prec |
PType |
precedence levels 0..4 |
TermPrec |
Type |
string with precedence |
mkPrec |
Prec -> Str -> TermPrec |
construct a TermPrec |
top |
TermPrec -> Str |
top term (lowest prec.) |
constant |
Str -> TermPrec |
atomic (highest prec.) |
infixl |
Prec->Str->(_,_:TermPrec)->TermPrec |
left-assoc. infix |
infixr |
Prec->Str->(_,_:TermPrec)->TermPrec |
right-assoc. infix |
infixn |
Prec->Str->(_,_:TermPrec)->TermPrec |
non-assoc. infix |
usePrec |
Prec -> TermPrec -> Str |
use term on given level |
The Symbolic module
This module is used for embedding symbolic notation in natural-language text constructed by the resource grammar API. It works for all resource languages.
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
symb |
Str -> NP |
x |
symb |
Int -> NP |
23 |
symb |
Float -> NP |
0.99 |
symb |
CN -> Numeral -> NP |
level four |
symb |
Det -> N+ -> Numeral -> NP |
the level four |
symb |
Det -> CN -> [Symb] -> NP |
the levels i, j and k |
symb |
Symb -> S |
A (formula) |
symb |
Symb -> Card |
n (number) |
mkSymb |
Str -> Symb |
x |
The Combinators module
This module gives shortcuts for defining predicates (pred) and function expressions (app). It works for all resource languages.
| Function | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
pred |
V -> NP -> Cl |
x converges |
pred |
V2 -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
x intersects y |
pred |
V -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
x and y intersect |
pred |
A -> NP -> Cl |
x is even |
pred |
A2 -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
x is divisible by y |
pred |
A -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
x and y are equal |
pred |
N -> NP -> Cl |
x is a maximum |
pred |
N -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
x and y are inverses |
pred |
Adv -> NP -> Cl |
x is in scope |
pred |
Prep -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
x is outside y |
app |
N -> NP |
the bottom |
app |
N2 -> NP -> NP |
the successor of x |
app |
N3 -> NP -> NP -> NP |
the distance from x to y |
app |
N2 -> NP -> NP -> NP |
the sum of x and y |
app |
N2 -> N -> CN |
set of integers |
app |
N2 -> NP -> CN |
divisor of x |
app |
N3 -> NP -> NP -> CN |
path from x to y |
app |
N2 -> NP -> NP -> CN |
path between x and y |
Browsing the libraries with GF commands
Note: You can browse using the syntax editor directly on the web.
All of the following assume that GF_LIB_PATH points to the directory GF/lib with compiled libraries.
To try out inflection paradigms:
> i -retain alltenses/ParadigmsGer.gfo
> cc mkN "Farbe"To try out overloaded syntax, test lexicon, and inflection paradigms:
> i -retain alltenses/TryGer.gfo
> cc mkCl (mkNP this_Quant (mkN "Farbe")) (mkA "dunkel")An Example of Usage
The standard way of building an application has the following modules.
An abstract syntax:
abstract Music = {
cat
Kind ;
Property ;
fun
PropKind : Kind -> Property -> Kind ;
Song : Kind ;
American : Property ;
}A domain lexicon interface:
interface LexMusic = open Cat in {
oper
song_N : N ;
american_A : A ;
}A functor on Syntax and the domain lexicon interface:
incomplete concrete MusicI of Music = open Syntax, LexMusic in {
lincat
Kind = CN ;
Property = AP ;
lin
PropKind k p = mkCN p k ;
Song = mkCN song_N ;
American = mkAP american_A ;
}For each language, an instance of the domain lexicon:
instance LexMusicGer of LexMusic = CatGer ** open ParadigmsGer in {
oper
song_N = mkN "Lied" "Lieder" neuter ;
american_A = mkA "amerikanisch" ;
}For each language, an instantiation of the functor:
--# -path=.:present:prelude
concrete MusicGer of Music = MusicI with
(Syntax = SyntaxGer),
(LexMusic = LexMusicGer) ;Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Categories
- Syntax Rules and Structural Words
- A - one-place adjective
- A2 - two-place adjective
- ACard - adjective like cardinal
- AP - adjectival phrase
- AdA - adjective-modifying adverb
- AdN - numeral-modifying adverb
- AdV - adverb directly attached to verb
- Adv - verb-phrase-modifying adverb
- Ant - anteriority
- CAdv - comparative adverb
- CN - common noun (without determiner)
- Card - cardinal number
- Cl - declarative clause, with all tenses
- ClSlash
- Comp - complement of copula, such as AP
- Conj - conjunction
- DAP - determiner with adjective
- Det - determiner phrase
- Dig
- Digits - cardinal or ordinal in digits
- IAdv - interrogative adverb
- IComp - interrogative complement of copula
- IDet - interrogative determiner
- IP - interrogative pronoun
- IQuant
- Imp - imperative
- ImpForm
- Interj - interjection
- ListAP
- ListAdv
- ListNP
- ListRS
- ListS
- N - common noun
- N2 - relational noun
- N3 - three-place relational noun
- NP - noun phrase (subject or object)
- Num - number determining element
- Numeral - cardinal or ordinal in words
- Ord - ordinal number (used in Det)
- PConj - phrase-beginning conjunction
- PN - proper name
- Phr - phrase in a text
- Pol - polarity
- Predet - predeterminer (prefixed Quant)
- Prep - preposition, or just case
- Pron - personal pronoun
- Punct
- QCl - question clause, with all tenses
- QS - question
- Quant - quantifier ('nucleus' of Det)
- RCl - relative clause, with all tenses
- RP - relative pronoun
- RS - relative
- S - declarative sentence
- SC - embedded sentence or question
- SSlash
- Sub100
- Sub1000
- Subj - subjunction
- Temp - temporal and aspectual features
- Tense - tense
- Text - text consisting of several phrases
- Unit
- Utt - sentence, question, word...
- V - one-place verb
- V2 - two-place verb
- V2A - verb with NP and AP complement
- V2Q - verb with NP and Q complement
- V2S - verb with NP and S complement
- V2V - verb with NP and V complement
- V3 - three-place verb
- VA - adjective-complement verb
- VP - verb phrase
- VPSlash - verb phrase missing complement
- VQ - question-complement verb
- VS - sentence-complement verb
- VV - verb-phrase-complement verb
- Voc - vocative or "please"
- Lexical Paradigms
- Paradigms for Afrikaans
- Paradigms for Arabic
- Paradigms for Bulgarian
- Paradigms for Catalan
- Paradigms for Chinese (simplified)
- Paradigms for Czech
- Paradigms for Danish
- Paradigms for Dutch
- Paradigms for English
- Paradigms for Estonian
- Paradigms for Basque
- Paradigms for Finnish
- Paradigms for French
- Paradigms for German
- Paradigms for Greek
- Paradigms for Hindi
- Paradigms for Icelandic
- Paradigms for Italian
- Paradigms for Japanese
- Paradigms for Latin
- Paradigms for Latvian
- Paradigms for Maltese
- Paradigms for Mongolian
- Paradigms for Nepali
- Paradigms for Norwegian (nynorsk)
- Paradigms for Norwegian (bokmål)
- Paradigms for Persian
- Paradigms for Punjabi
- Paradigms for Polish
- Paradigms for Portuguese
- Paradigms for Romanian
- Paradigms for Russian
- Paradigms for Slovak
- Paradigms for Sindhi
- Paradigms for Spanish
- Paradigms for Swedish
- Paradigms for Thai
- Paradigms for Urdu
- Additional Libraries
- Browsing the libraries with GF commands
- An Example of Usage
- Table of Contents